Fig. 3.
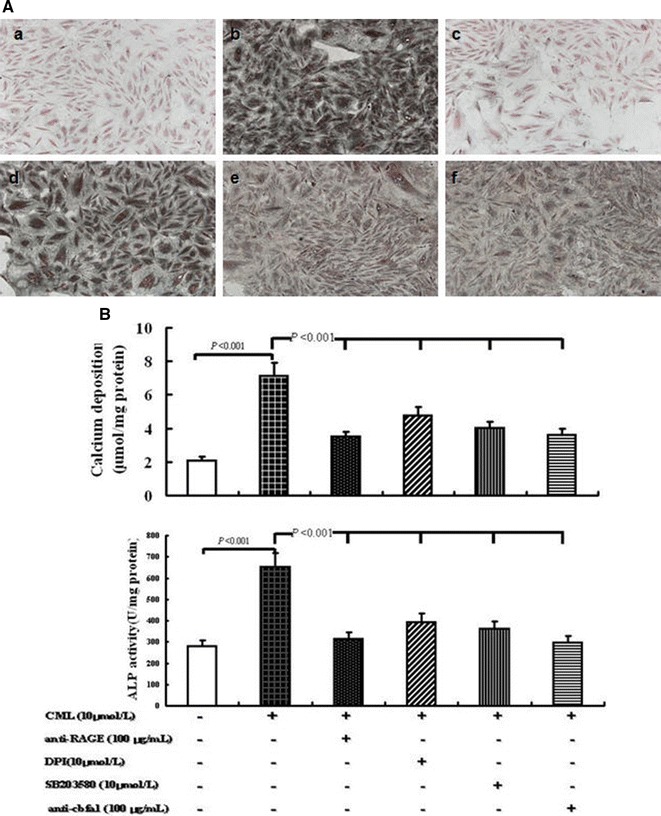
Effects of different treatments on VSMC calcification under high-lipid, apoptosis-coexisting conditions. A Morphology of calcified A7r5 cells was detected by von Kossa staining at the light microscopic level (×100). a Control group (A7r5 medium supplemented with 80 μg/mL RAW264.7-derived-ABs plus 50 μg/mL oxLDL); b CML group (A7r5 medium supplemented with 80 μg/mL RAW264.7-derived-ABs plus 50 μg/mL oxLDL and 10 μmol/L CML); c anti-RAGE group (A7r5 medium supplemented with 80 μg/mL RAW264.7-derived-ABs plus 50 μg/mL oxLDL, 10 μmol/L CML, and 100 μg/mL antibody against RAGE); d NADPH oxidase inhibitor group (A7r5 medium supplemented with 80 μg/mL RAW264.7-derived-ABs plus 50 μg/mL oxLDL, 10 μmol/L CML, and 10 μmol/L DPI); e p38MAPK inhibitor group (A7r5 medium supplemented with 80 μg/mL RAW264.7-derived-ABs plus 50 μg/mL oxLDL, 10 μmol/L CML, and SB203580); f anti-cbfα1 group (A7r5 medium supplemented with 80 μg/mL RAW264.7-derived-ABs plus 50 μg/mL oxLDL, 10 μmol/L CML, and 100 μg/mL antibody against cbfα1). Cells in each group were cultured for 7 days, and the medium was replaced every 2 days. B Calcium depositions were measured utilizing the O-cresolphthalein complexone method and normalized in accordance with the cellular protein content. The activity of ALP was analyzed by ALP activity assay kit. Cells were treated similar to A. Values are expressed as mean ± SD from the three independent experiments
