Fig. 3.
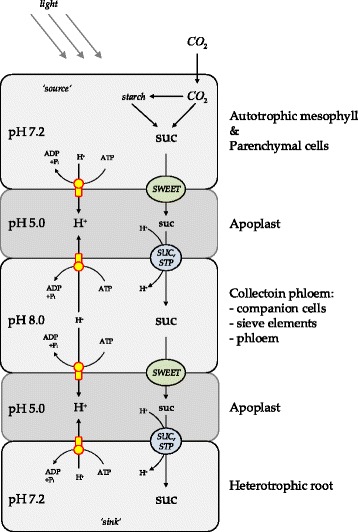
Simplified mechanism of sucrose translocation from autotrophic to heterotrophic tissues via connecting tissue. The autotrophic tissue (mesophyll) synthesises sucrose that is translocated to heterotrophic tissue (root) as carbon and energy source to build biomass. Metabolically active tissues form a proton gradient with the extracellular space (apoplast), which is used by the sink tissue to uptake sucrose. suc – sucrose, H + – proton, SWEET – sucrose efflux transporters, SUC,STP – sucrose-proton symporters. Size of letters represents relative concentrations
