Figure 2.
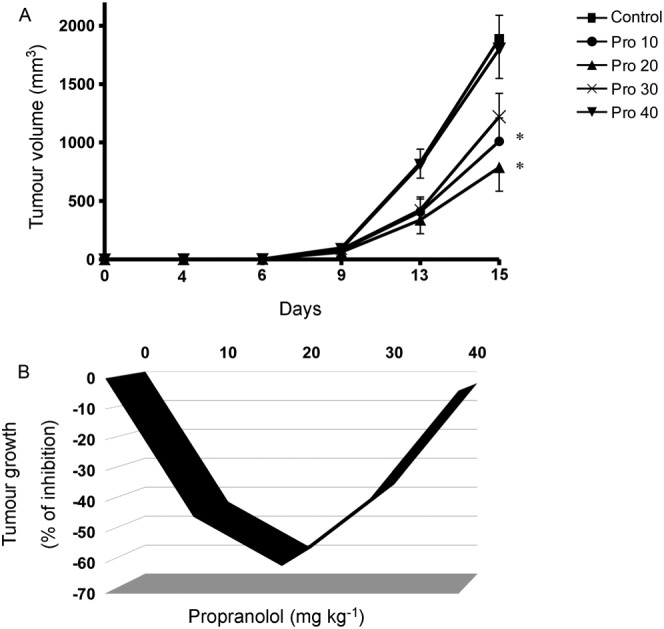
Biphasic effect of propranolol on melanoma growth. (A) Tumour volume. B16F10 tumour‐bearing mice were treated with vehicle (Control) or with increasing doses of propranolol (10, 20, 30 and 40 mg·kg−1·day−1). Propranolol was administered via i.p. route once daily for 15 days. Maximal inhibition of tumour growth was obtained at the dose of 20 mg·kg−1·day−1. Data represent mean tumour volume ± SEM (n = 6 per group). * P < 0.05, significantly different from the control group). (B) Tumour inhibition rate. Data were calculated by using the equation 100 − (T/C*100), where T is the mean volume of the treated tumour and C is the mean volume in the control group at the day 15 after tumour cell inoculation. Propranolol inhibits tumour growth in mice in a U‐shaped biphasic manner. Control, saline‐treated mice; Pro 10, mice treated with 10 mg·kg−1·day−1; Pro 20, mice treated with 20 mg·kg−1·day−1; Pro 30, mice treated with 30 mg·kg−1·day−1; Pro 40, mice treated with 40 mg·kg−1·day−1.
