Figure 7.
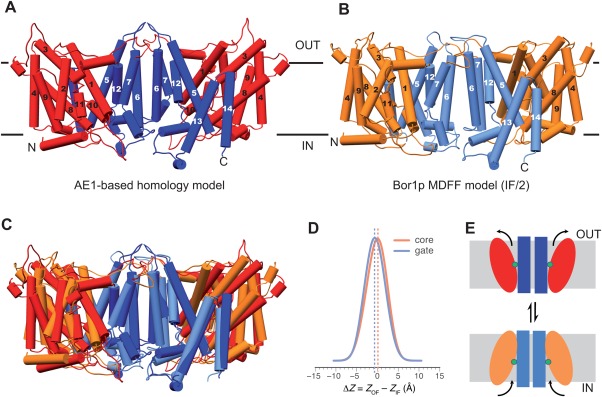
Comparison of outward‐facing and inward‐facing conformations. (A) Homology model of Bor1p obtained from MODELLER using the outward‐facing AE1 structure as a template. Transmembrane helices, which are essentially identical to those seen in the AE1 structure, are numbered according to Supporting Information Figures S3 and S4. Gate domains are colored blue and core domains are red. (B) Bor1p model (IF/2) in an inward‐facing conformation as determined from tubular crystals. Gate and core domains are colored blue and orange. (C) Overlay of outward‐ and inward‐facing conformations. The gate domains are closely aligned, whereas the core domain has a different inclination. There does not appear to be any vertical displacement of the core domain across the membrane. (D) Distribution of differences resulting from the comparison of gate and core domains in outward‐ vs. inward‐facing conformations as determined from MD simulations (see Supporting Information Fig. S9). Both the core (orange) and the gate domain (blue) shift by less than 1 Å relative to the membrane in comparing these two conformations, and even less relative to each other, confirming the lack of vertical displacement that would be expected from an elevator‐type mechanism. (E) Cartoon depicting the inclination of core domain that we propose converts Bor1p from inward‐facing to outward‐facing conformation.
