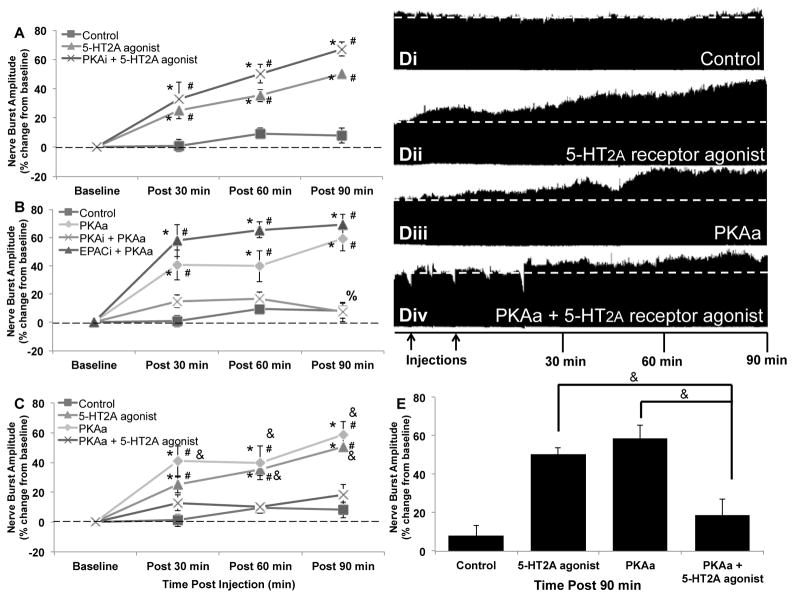
Figure 1. PKA constrains 5-HT2A receptor-induced phrenic motor facilitation.
A) intermittent intrathecal injections of 5-HT2A receptor agonist (3×6μL, 100μM) elicited pMF (90min: 50.6 ± 3.1%; n = 6; p < 0.001) were not affected by PKAi (10μL, 1mM; 90min: 67.2 ± 4.9%; n = 5; p = 0.098 relative to 5-HT2A agonist induced pMF). B) Intrathecal injections of PKAa (10μL, 100μM) elicited pMF (90min: 58.9 ± 8.6%; n = 7; p < 0.001), an effect that was undermined by PKAi (90min: 7.3 ± 6.7%; n = 6; p < 0.001), but not EPACi pretreatment (90min: 69.1 ± 7.3%; n = 4; p = 0.819). C) Concurrent application of PKAa and 5-HT2A receptor agonist limited the capacity for either to elicit pMF (90min: 18.6 ± 6.5%; n = 7; p < 0.001 relative to PKAa or 5-HT2A receptor agonist-induced pMF). D) Representative phrenic neurograms; i) vehicle control, ii) vehicle + 5-HT2A receptor agonist, iii) vehicle + PKAa and iv) PKAa + 5-HT2A receptor agonist. First arrow represents pretreatment injection; second arrow represents either start of intermittent 5-HT2A agonist injections or start of single PKAa injection. E) Summary of data from A–C at 90min post-final injection. Data represent mean values ± 1 SEM. Significant differences from baseline (#), control (*), PKAa (%), or PKAa + 5-HT2A receptor agonist (&).