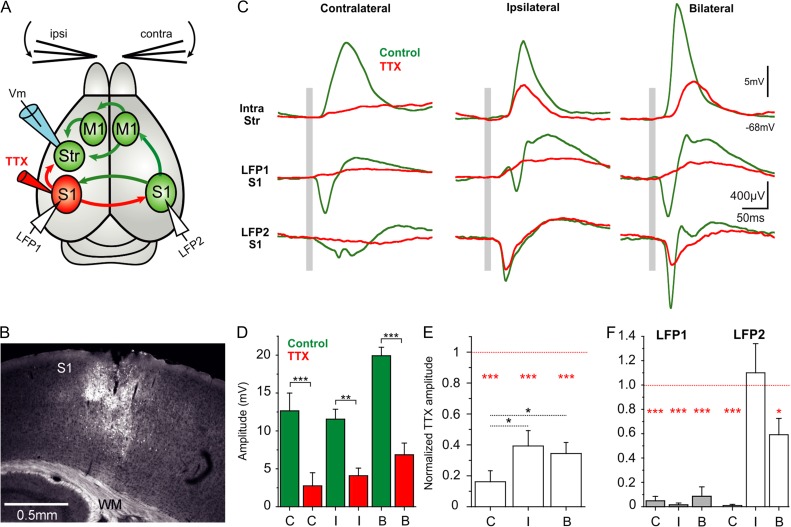
Figure 6.
Blocking ipsilateral S1 reduces responses to both ipsi- and contralateral whisker stimulation. (A) Diagram of the experimental configuration and main synaptic pathways; arrows in red show the synaptic outputs blocked by TTX injection to ipsilateral S1. Unblocked regions and pathways (green) and recording electrodes in dorsolateral striatum and S1 of both cortical hemispheres. (B) Example of a TTX (10 µM) and neurobiotin (0.4%) injection-site in ipsilateral S1. (C) Waveform average (>40 repetitions) of a whole-cell recorded MSN with simultaneous cortical LFP recordings in response to contra-, ipsi-, and bilateral whisker deflection before and after injection of TTX 10 µM in ipsilateral S1. The gray bar represents the air-puff whisker deflection. (D) Absolute response amplitude to contra-, ipsi-, and bilateral whisker deflection before and after TTX application in ipsilateral S1 (n = 6 animals). (E) Normalized amplitude change in striatal whole-cell recordings. The normalization was done with respect to the control condition for each neuron and type of stimulation (n = 6). (F) Normalized amplitude with respect to the control condition for each LFP recording in the right and left cortical hemisphere and type of stimulation (n = 6). All responses are measured during down states. Asterisks *, **, *** represent P values <0.05, <0.01, <0.001, respectively.