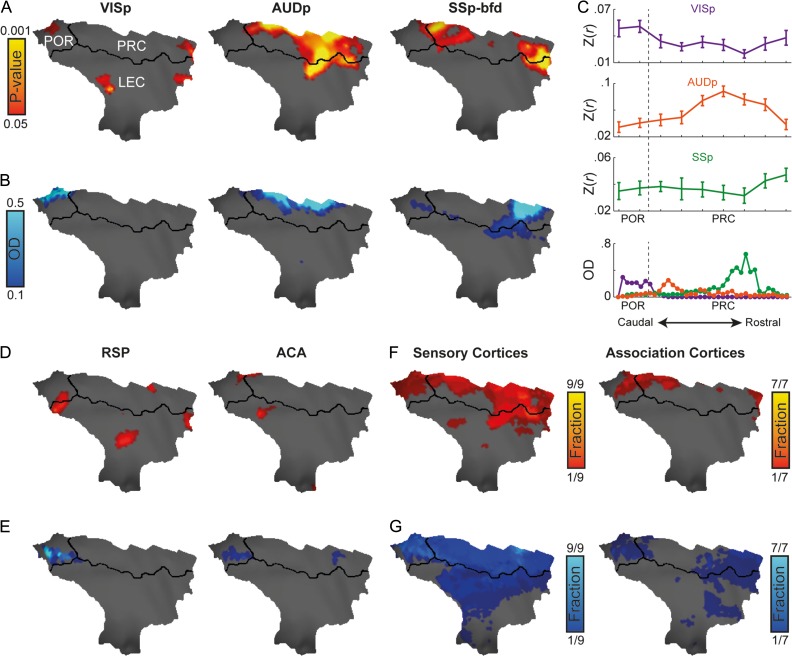
Figure 3.
Convergence of sensory and association networks as opposed to spatially localized sensory mapping in the mouse parahippocampal region. (A) Functional connectivity of primary visual (VISp, left), auditory (AUDp, center) and barrel-related somatosensory (SSp-bfd, right) cortices and parahippocampal region, P < 0.05 corrected for multiple comparisons using family-wise error rate correction for the hippocampal memory system. (B) Anatomical connections between primary visual, auditory, and somatosensory cortices and the parahippocampal region. (C) Volume-based quantification of the average correlations (top) and normalized optical density (bottom) of different sensory modalities along the longitudinal axis of the parahippocampal region. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean. Functional (D) and anatomical connectivity (E) of the retorsplenial (RSP, left) and anterior cingulate (ACA, right) cortices in the parahippocampal region (similar to C, D). Functional (F) and anatomical (G) fractions of sensory (left) and association (right) regions cover the mouse parahippocampal region. In regions that contain several seeds, the functional and anatomical maps were averaged; same thresholds from (A, D) and (B, E) were used as binary thresholds for the functional and anatomical data, respectively.