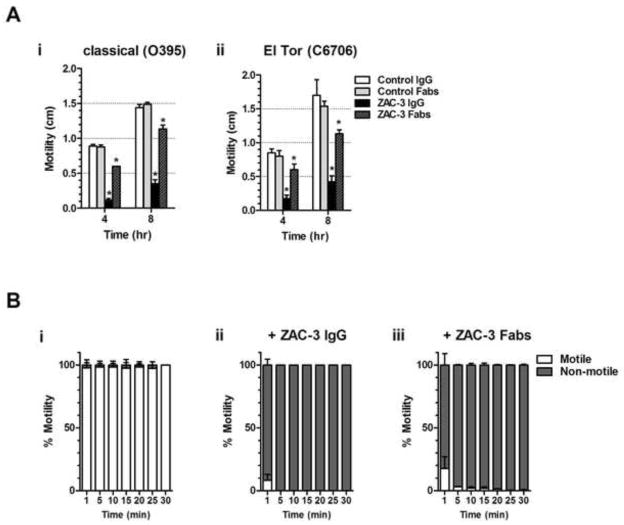
Figure 1. ZAC-3 IgG and Fab fragments inhibit motility of V. cholerae classical and El Tor biotypes.
(A) V. cholerae motility assays in semi-solid LB agar (0.3%) containing IgG or Fabs of ZAC-3 or isotype controls, as described [14]. Isotype controls included recombinant human IgG1 MAbs directed against Salmonella O5 antigen (Sal4) (manuscript in preparation) or ricin toxin (PB10) [20]. A single colony of V. cholerae strain O395 (panel A.i) or C6707 (panel A.ii) was used to stab inoculate the center of LB agar plates, which were placed at 37°C. Bacterial migration away of the point of inoculation was assessed at 4 and 8 h time points. A minimum of three independent experiments was performed for each antibody treatment. The Student’s t test was used to determine statistical significance between ZAC-3 IgG and Fab fragment treatment compared to their respective controls (*, P<0.05, **, P<0.01). (B) Live digital microscopy of V. cholerae motility in liquid medium containing an isotype control (panel B.i), ZAC-3 IgG (panel B.ii) or ZAC-3 Fab fragments (panel B.iii), was performed as described [14]. For each antibody treatment, three independent videos containing 100 image sequences were acquired (7.14 frames per second) every 5 min for a total of 30 min. Within each 100 frame video, 3 sets of 6 frames were selected throughout the video and the number of bacteria observed moving between each frame and not moving between each frame was quantitated using Fiji software version 1.49f [21]. Percent motility was calculated using the average number of motile bacteria over the total number of bacteria seen in the selected frames. The mean (bars) and standard deviation (error bars) from the three videos for each treatment are shown in the graph. All IgG and Fab treatments presented in panels Bii and Biii resulted in a significant reduction in motility as compared to control samples (*P<0.0001, Student’s t test).