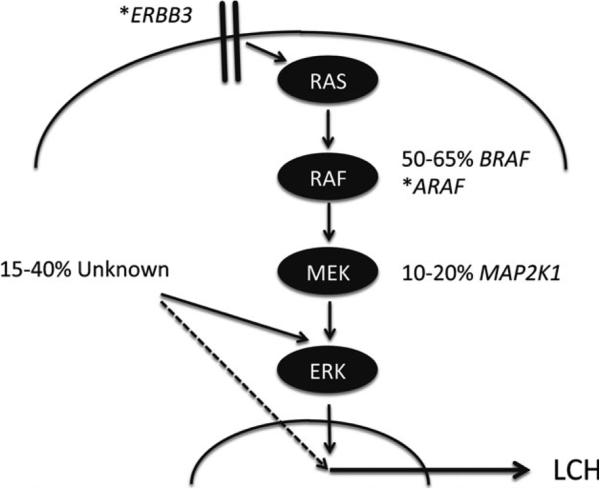
Fig 1.
Routes to ERK activation in LCH. Model of MAPK pathway activation resulting from serial phosphorylation from cellular receptors through RAS, RAF, MEK and, ultimately, ERK. Estimates of frequency of somatic mutations of BRAF and MAP2K1 are illustrated. (*) indicates genes with individual case reports of somatic mutations. ‘Unknown’ indicates ERK activation by mechanisms that have not yet been defined. While activated ERK has been identified in all lesions studied to date, there remains the possibility (dashed line) that Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) may arise from alternative mechanisms in some cases.