Figure 5.
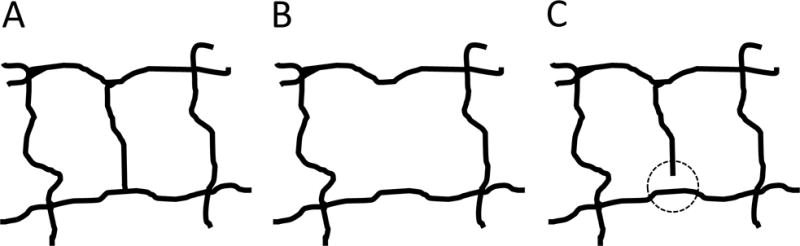
Pictorial explanation of the advantages of intercapillary area based techniques over vessel density based techniques. (A) Hypothetical healthy vascular structure. Here, there are two intercapillary areas, both of roughly equal size. (B) The center capillary is lost, creating a single intercapillary area of roughly double the size. Thus, the largest intercapillary area would double; however, the vessel density does not change by a commensurate amount. Herein lies the advantage of intercapillary area based techniques: relatively small changes in vessel density can cause much larger changes in intercapillary area. (C) The increased sensitivity comes at a cost: if there is an error in segmentation, seen here as a small discontinuity inside the dashed circle, the intercapillary area doubles, while the vessel density remains virtually unaffected. Thus, vessel density based techniques have a robustness advantage compared to intercapillary area techniques.
