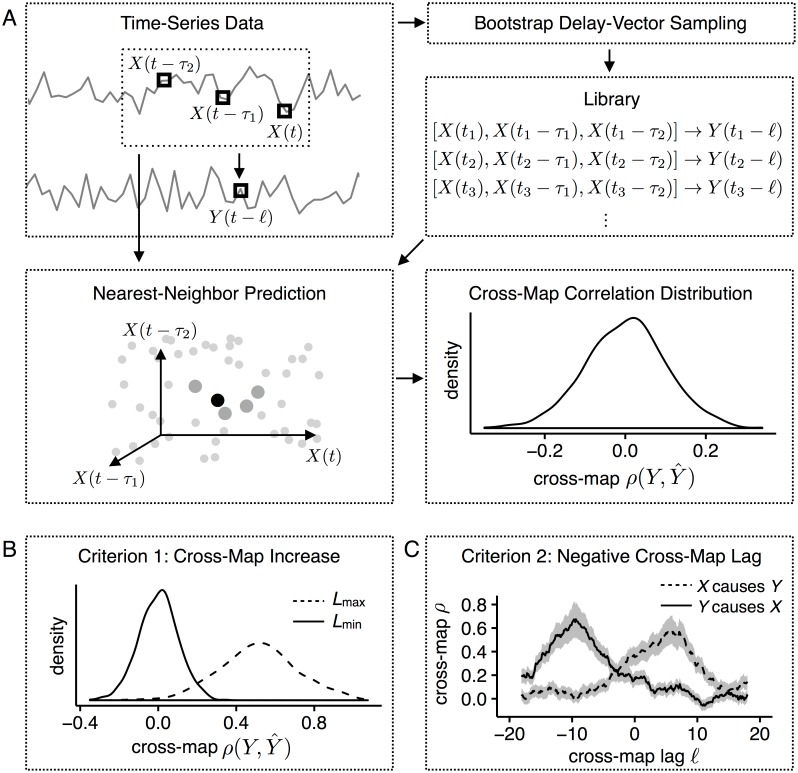
Fig 1. Summary of criteria for detecting causality.
(A) Schematic of cross-map algorithm for testing Y → X. Delay vectors in X, mapped to values in Y with lag ℓ, are bootstrap-sampled to construct a prediction library. For each delay vector in X, reconstructed values are calculated from a distance-weighted sum of Y values from nearest neighbors in the library. Many sampled libraries yield a distribution of cross-map correlations between actual Y and reconstructed . (B) Criterion 1 (cross-map increase). Bootstrap distributions of cross-map correlation are calculated at minimum and maximum library sizes with ℓ = 0; causality is inferred if the correlation at Lmax is significantly greater than the correlation at Lmin. (C) Criterion 2 (negative cross-map lag). Cross-map correlations are calculated across different values of ℓ. Causality is inferred if the highest cross-map correlation for negative ℓ is positive and significantly greater than the highest value for nonnegative ℓ.