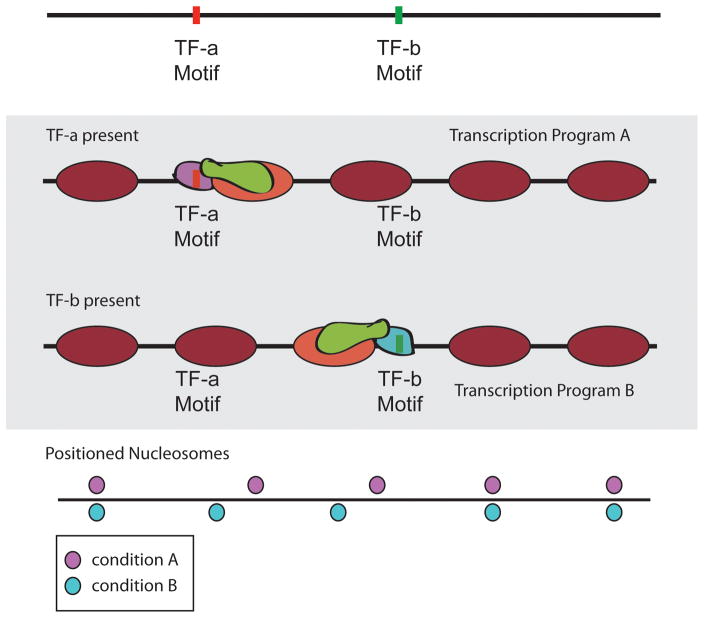
Figure 5.
Sequence-targeted chromatin remodeling allows for nucleosome positioning plasticity in different conditions. Top: Schematic of two hypothetical transcription factor (TF) binding sites on a DNA strand. Middle: Hypothetical nucleosome positions if a chromatin remodeling factor is targeted through TF-a or TF-b in a condition where the competing TF is not present. Bottom: Comparison of nucleosome positions under two distinct environmental conditions established through sequence-targeted chromatin remodeling.