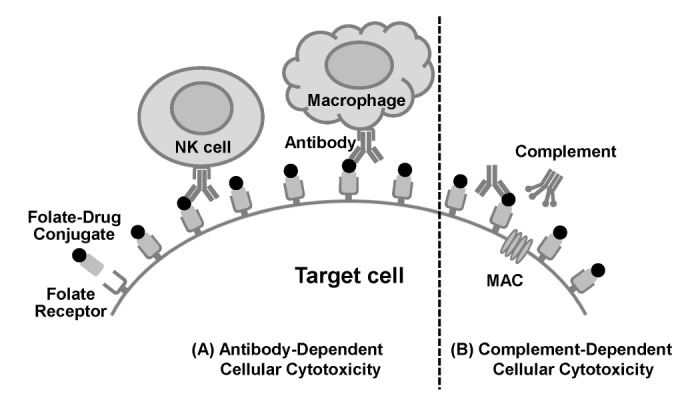
Figure 2. (A) Folate receptor (FR)-targeted immunotherapy by antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) by NK cells and macrophages. A folate-hapten conjugate binds with the FR on target cells, and antibodies specific for the hapten directly bind with the hapten on the conjugate. Macrophages and NK cells then recognize the antibody through their Fc receptors and kill the target cells by ADCC. (B) FR-targeted immunotherapy by complement-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (CDC). A folate-hapten conjugate binds with the FR on target cells and antibodies specific for the hapten bind directly to it. Complement components then bind to the antibody, and this binding activates complement cascades, followed by the formation of a membrane attack complex (MAC) at the surface of the target cells, which leads to cell death.