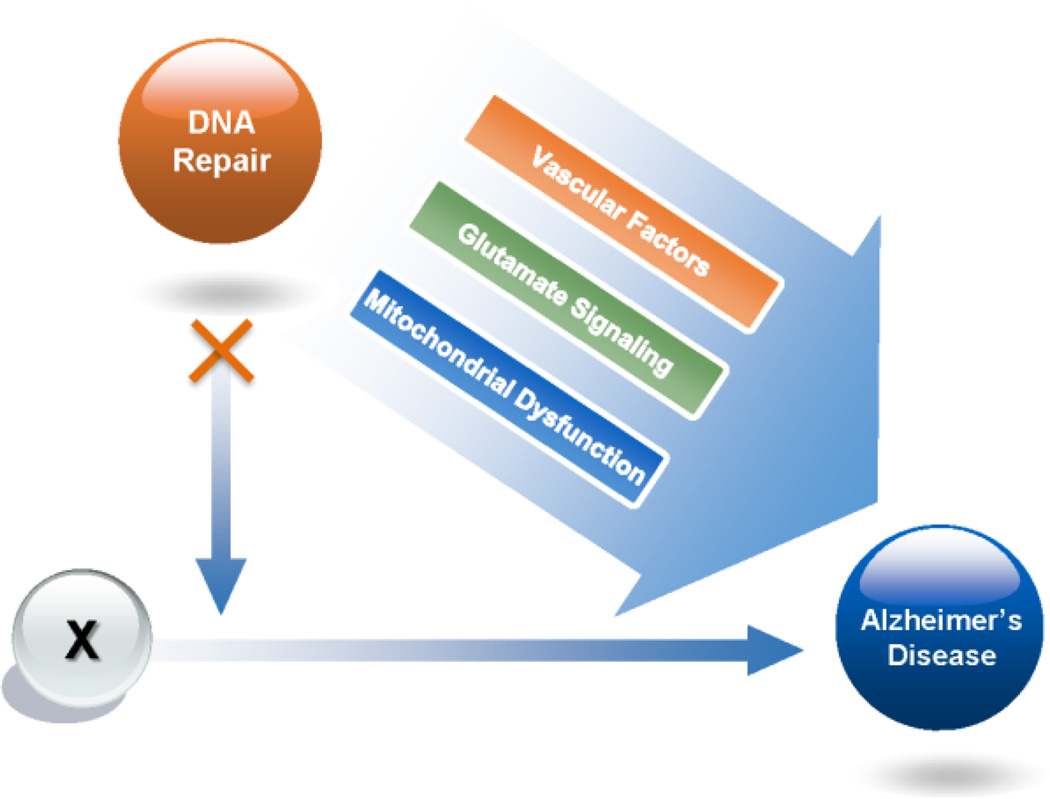
Figure 2. How DNA repair plays a role in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease.
Since there are several different hypotheses about the origins of AD, we have used an “X” to represent the initiation of AD. Loss of DNA repair may exacerbate Alzheimer’s disease through multiple pathways including changes in vascular factors, glutamate signaling, nuclear and mitochondria DNA damage and repair pathways.