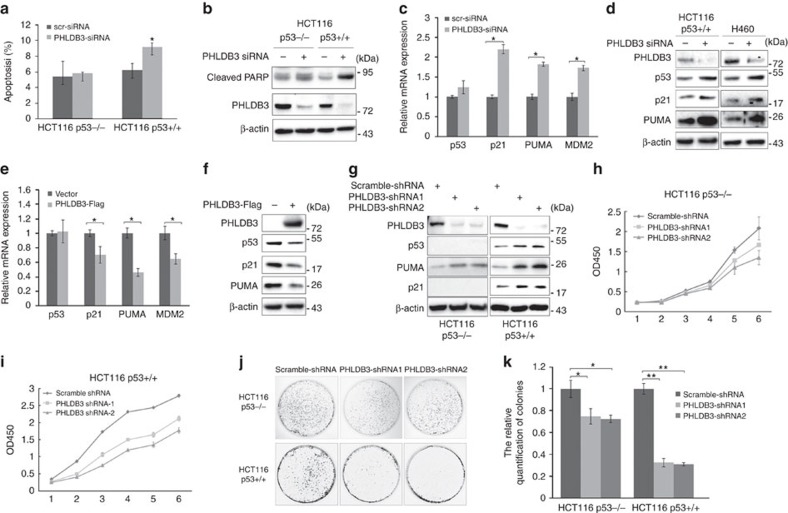
Figure 4. PHLDB3 knockdown inhibits cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis of colon cancer cells by inducing p53 protein level.
(a,b) The effect of PHLDB3 knockdown on apoptosis of HCT116p53−/− and HCT116p53+/+ cells. HCT116p53−/− and HCT116p53+/+ cells were transfected with PHLDB3 or scramble siRNA and harvested 72 h post-transfection for flow cytometry analysis (a) or immunoblotting with indicated antibodies (b). Quantification of Sub-G1 population is shown in a. (c–f) Knockdown of PHLDB3 induces, but overexpression of PHLDB3 reduces, p53 and its target genes. HCT116p53+/+ (c,d) and H460 (d) cells were transfected with PHLDB3 or scramble siRNA and harvested 72 h post transfection for RT-qPCR (c) or immunoblotting with indicated antibodies (d). HCT116p53+/+ cells were transfected with PHLDB3-Flag or vector plasmid and harvested 48 h post transfection for RT-qPCR (e) or immunoblotting with indicated antibodies (f). (g) Knockdown of PHLDB3 causes p53-dependent induction of p21 and Puma. The protein levels of p53 and its targets, p21 and Puma, in HCT116p53−/− and HCT116p53+/+ cells that stably expressed PHLDB3 or scramble shRNA were detected by immunoblotting using antibodies as indicated. (h,i) The effect of PHLDB3 knockdown on colon cancer cell growth. HCT116p53−/− (h) and HCT116p53+/+ (i) cells that stably expressed PHLDB3 or scramble shRNA were seeded in 96-well plate and cell viability was evaluated every 24 h by CCK8. (j,k) Knockdown of PHLDB3 leads to inhibition of clonogenic capability of colorectal cancer cells, more significantly when the cells harbor wild type p53. HCT116p53−/− and HCT116p53+/+ cells that stably expressed PHLDB3 shRNA were seeded on 10-cm plates for 10–14 days, and colonies were fixed by methanol and stained with crystal violet solution (j). The relative quantification of colonies is shown in k. Where applicable, data represent mean±s.e.m. of triplicate experiments.*P<0.05, **P<0.01 by two-tailed t-test (a,c,e,k).