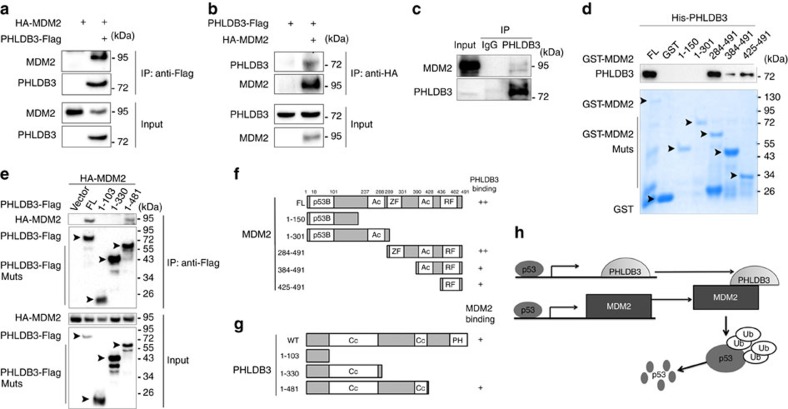
Figure 6. PHLDB3 interacts with MDM2.
(a,b) The interaction between ectopic PHLDB3 and MDM2. HEK293 cells were transfected with plasmids encoding PHLDB3-Flag and/or HA-MDM2 as indicated followed by Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) assays using antibodies as indicated. (c) The association between endogenous PHLDB3 and MDM2 is detected after treatment of HCT116p53+/+ cells with Doxorubicin. HCT116p53+/+ cells were treated with Doxorubicin for 16 h and MG132 for 6 h before harvested for co-IP-IB assays using antibodies as indicated. IgG was used as a control. (d) Mapping the PHLDB3 binding domain of MDM2 by GST-pull down assays. Purified GST-tagged MDM2 fragments, including aa 1–150, aa 1–301, aa 284–491, aa 384–491 or aa 425–491, and GST protein alone were incubated with purified His-PHLDB3 for one hour at room temperature. Bound proteins were detected by immunoblotting using anti-PHLDB3 or coomassie staining. (e) Mapping the MDM2 binding domain of PHLDB3 by Co-immunoprecipitation. HCT116p53−/− cells were transfected with an HA-MDM2-encoded plasmid along with the plasmid encoding each individual Flag-tagged PHLDB3 fragment as indicated. Co-IP assays were performed using the anti-Flag antibody followed by IB with the anti-HA antibody. (f) A schematic diagram of PHLDB3 binding regions on MDM2 based on the result from d. (g) A schematic diagram of MDM2 binding regions on PHLDB3 based on the result from e. (h) A model for the negative feedback regulation of p53 by the PHLDB3 and MDM2 complex.