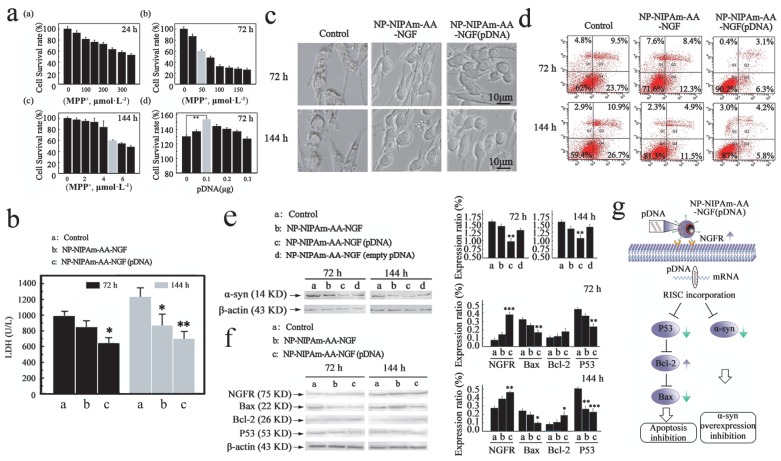
Figure 2.
Measured efficacy data in vitro. (a), Cellular apoptosis model induced by MPP+ at 24 h, 72 h and 144 h, and pDNA concentration screening. (b), The LDH expression determined using the LDH detection kit for the control, NP-NIPAm-AA-NGF and NP-NIPAm-AA-NGF (pDNA) group at 72 h and 144 h. (c), Cell morphology evaluated by light microscopy (black bars, 10 μm). (d), Cell mortality data assessed by flow cytometry in the three groups: control, NP-NIPAm-AA-NGF, and NP-NIPAm-AA-NGF (pDNA) at 72 h and 144 h. (e), Protein expression of α-syn by western blot analysis in the control, NP-NIPAm-AA-NGF, NP-NIPAm-AA-NGF (pDNA) and NP-NIPAm-AA-NGF (empty pDNA) groups at 72 h and 144 h. (f), Protein expression of NGFR, Bax, Bcl-2, and P53 determined by western blot analysis in the control, NP-NIPAm-AA-NGF and NP-NIPAm-AA-NGF (pDNA) groups at 72 h and 144 h. The blots were re-probed to detect β-actin as a control to confirm equal protein loading. Protein expression determined using Image pro-plus 6.0. (g). The possible molecular mechanisms for multifunctional nano-biomaterials release α-syn interference plasmid to inhibit the synthesis of α-syn. The relative levels are plotted at a significance of p < 0.05 indicated by *, 0.001 < p < 0.01 indicated by **, and p < 0.001 indicated by ***, in comparison to the control group.