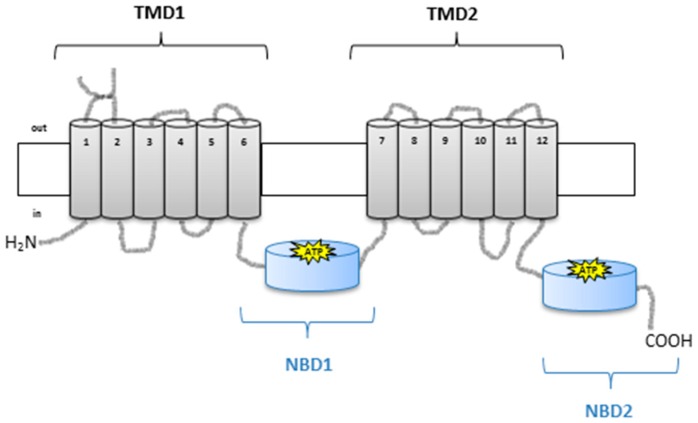
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) structure with two halves, each with a transmembrane domain (TMD1 and TMD2) and a nucleotide-binding domain (NBD1 and NBD2) (adapted from [5]). The transmembrane domains (TMDs)—composed of six membrane α-helices (TM1–TM6 and TM7–TM12)—contain the drug binding sites and define the translocation pathway across the membrane; the two cytoplasmic nucleotide-binding domains (NBDs) couple the energy associated with ATP binding and hydrolysis, which is necessary for drug transport [6].