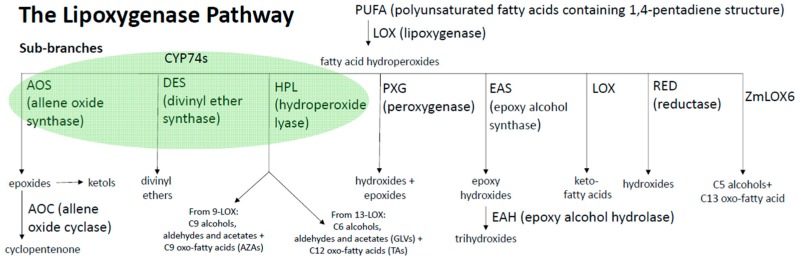
Figure 3.
Major metabolite classes produced by the eight sub-branches in the Lipoxygenase (LOX) pathway. LOXs catalyze the dioxygenation of polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA), namely linoleic (C18:2) or linolenic (C18:3) fatty acids at the 9- or 13-carbon position. The subsequent hydroperoxide fatty acid can be fluxed into seven sub-branches [31,46]. Allene oxide synthase (AOS), divinyl ether synthase (DES), and hydroperoxide lyase (HPL) are cytochrome P450 monooxygenases (CYP) and part of the CYP74 clade (green oval). The AOS sub-branch is responsible for production of jasmonates (JAs). Divinyl ether synthases (DES) have been identified in some dicots, but not in monocots, including maize. The hydroperoxide lyase (HPL) sub-branch mediates the cleavage of 13-hydroperoxide octadecadi(tri)enoic (HPOD/T) into C6- alcohols, aldehydes, and acetates collectively known as green leaf volatiles (GLVs), and as well as the oxo-fatty acid, traumatin which oxidizes into the dicarboxylic acid, traumatic acid (TA). 9-HPL converts 9-HPOD/T to produce C-9 alcohols, aldehydes, acetates, and C9-oxo-fatty acid that can be oxidized into the dicarboxylic acid, azelaic acid (AZA). Peroxygenase (PXG) catalyzes the formation of hydroxides and epoxides. LOX activity on hydroperoxides yields keto fatty acids. Epoxide alcohol synthase (EAS) synthesizes epoxy-hydroxides which are hydrolyzed to trihydroxy fatty acids. Hydroxides can be converted nonenzymatically from hydroperoxy fatty acids or through action of reductases. ZmLOX6 is a unique monocot specific sub-branch which produces a C13-oxo-fatty acid and C5 alcohols from 13-HPOT specifically [48].