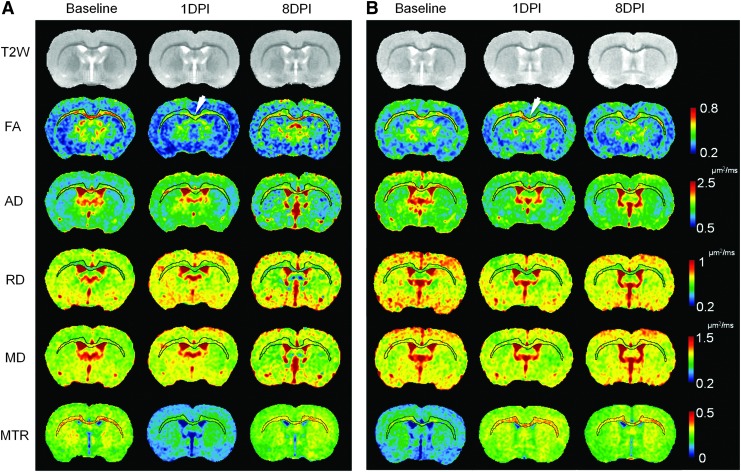
FIG. 3.
Longitudinal diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and magnetization transfer ratio (MTR) maps of the normal (A) and mild ventriculomegaly (MVM) (B) brain following mild traumatic brain injury (TBI). Corpus callosum and external capsule were segmented to highlight the pattern of diffuse axonal injury over time. Decreases of fractional anisotropy (FA) (arrow in A), axial diffusivity (AD), and MTR were clearly seen immediately after injury in the normal brain at 1 day post-injury (DPI), whereas radial diffusivity (RD), and mean diffusivity (MD) show changes and were scattered across multiple locations. MVM rat brains do not show the similar axonal injury pattern in the FA maps at 1 DPI (arrow in B). The MTR maps show dramatic different trends of contrast changes in the ventriculomegaly brain in response to mild TBI. Color image is available online at www.liebertpub.com/neu