Figure 7.
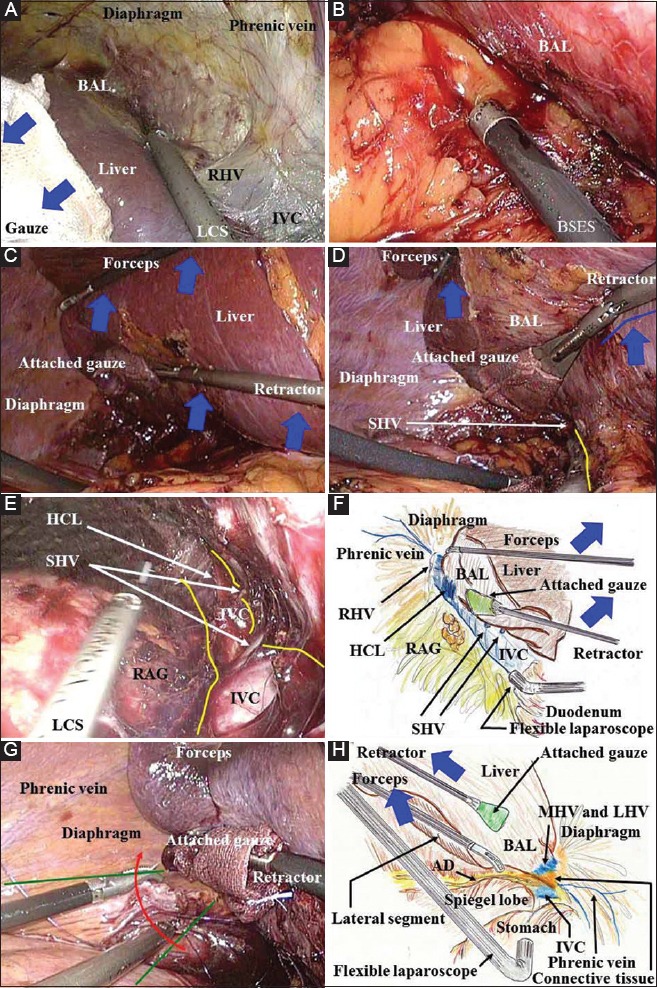
(A) During a hybrid technique/pure laparoscopic surgery, the specialized retractor shown in this figure ensures adequate retraction/countertraction of the liver without any slippage (blue arrows). Laparosonic coagulating shears serve as a useful scalpel that provides hemostasis for dissection around the inferior vena cava and exposure of the bare area of the liver. To expose the bare area of the liver in pure laparoscopic surgery or a hybrid technique, two working ports should be placed on the lateral-dorsal side and as far to the head side as possible. (B) During a hybrid technique/pure laparoscopic surgery, rubbing of a bleeding vessel or oozing tissue with a button-shaped electrode with suction and a soft-coagulation system is a key technique for reliable hemostasis. (C) During surgical procedures involving removal of the right lobe in a hybrid technique/pure laparoscopic surgery, an assistant surgeon should ensure adequate retraction of the liver using two forceps/retractors (blue arrows). (D, E) Under the liver retraction by an assistant during a hybrid technique/pure laparoscopic surgery (blue arrows and line), the inferior vena cava wall can be bared by laparosonic coagulating shears (yellow line). The short hepatic veins and hepatocaval ligament can be skeletonized. (F) In hybrid technique/pure laparoscopic surgery, the horizontal view from the para-inferior vena cava via a flexible laparoscope provides an excellent view along the inferior vena cava. The inferior vena cava is completely bared in the plain view. This view along the length of the vena cava is an advantageous point for the laparoscope. (G) During a hybrid technique/pure laparoscopic surgery, the laparoscopic surgical field essentially spreads to the foreground (green lines); therefore, a suture for hemostasis should be placed from the front side and from the bottom side (red arrows), using the front safety area. (H) The lateral view via a flexible laparoscope provides an excellent magnified field. The inferior vena cava wall should be bared at the upper side of Spiegel’s lobe after ligation of Arantius’ duct and complete dissection of the connective tissues AD, Arantius’ duct; BAL, bare area of the liver; BSES, button-shaped electrode with suction; HCL, hepatocaval ligament; HSE, hook-shaped electrode; HT, hybrid technique; IVC, inferior vena cava; LCS, laparosonic coagulating shears; LHV, left hepatic vein; MHV, middle hepatic vein; PLS, pure laparoscopic surgery; RAG, right adrenal gland; RHV, right hepatic vein; SHV, short hepatic vein
