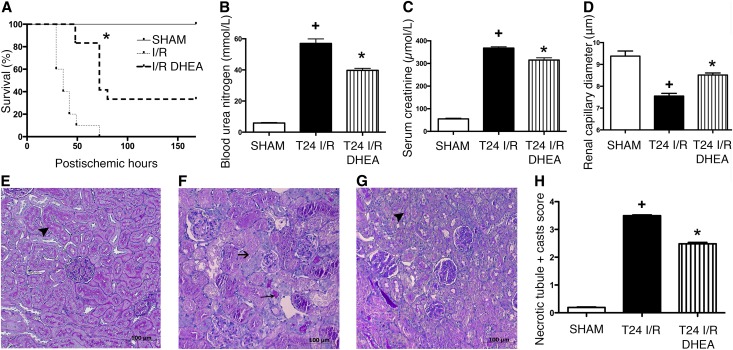
Figure 2.
DHEA pretreatment is protective against renal IRI. (A) Postischemic survival was followed for 7 days in rats pretreated with vehicle (I/R) or DHEA (I/R DHEA) 25 and 1 hour before the 50-minute ischemia. Log rank test (n=8 per group). *P<0.001 versus I/R. (B) BUN levels of vehicle (T24 I/R) and DHEA (T24 I/R DHEA) -pretreated rats after 24 hours of reperfusion. *P<0.05 versus T24 I/R (n=6 per group); +P<0.05 versus sham (n=6 per group). (C) Serum creatinine levels. *P<0.05 versus T24 I/R (n=6 per group); +P<0.05 versus sham (n=6 per group). (D) Renal capillary diameters measured using intravital two–photon microscopy. Approximately 150 capillaries per animal. Bars indicate means±SEMs, and data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni multiple comparison test. *P<0.05 versus T24 I/R (n=3 per group); +P<0.05 versus sham (n=3 per group). (E–G) Representative images of structural damage after IRI on PAS–stained kidney sections of (E) sham-operated, (F) T24 I/R, or (G) T24 I/R DHEA–pretreated rats. Black arrowheads points to intact brush border, long thin black arrow shows hyaline accumulation, and short black arrow shows necrotic tubule. Original magnification, ×200. (H) Semiquantitative evaluation of tubular injury on a zero to four scale. Bars indicate medians ± ranges, and data were analyzed by Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn correction. *P<0.05 versus T24 I/R (n=6 per group); +P<0.05 versus sham (n=6 per group).