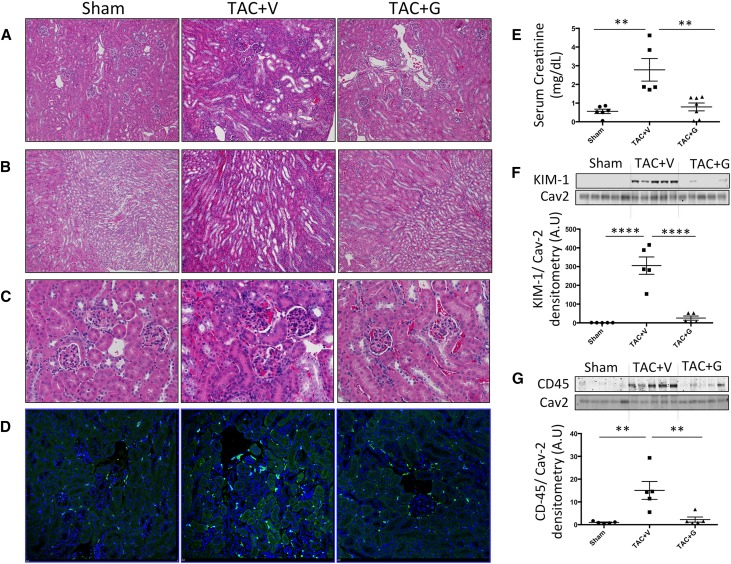
Figure 1.
CRS2 develops in chronic stages of the TAC CHF mouse model. Kidneys from mice 12 weeks post-TAC show focal tubular damage with tubular epithelial simplification and tubular loss in both (A) cortical and (B) medullary regions (hematoxylin-eosin–stained paraffin sections; ×10). (C) Hematoxylin-eosin–stained sections also show increased cellular infiltration in the glomerular and tubular regions (×40). (D) Immunofluorescence staining (×20) and (G) Western blotting analysis for CD45 expression show an increase in kidney inflammation in 12-weeks TAC CHF mice. These histopathologic findings were accompanied by (E) worsening renal function as indicated by the elevated serum creatinine in these mice and (F) renal tissue damage as indicated by the elevated protein expression of KIM-1. All of these pathologic changes are attenuated by gallein treatment. Vehicle or gallein (10 mg/kg per day intraperitoneally) treatment was initiated 4 weeks post-TAC and continued until 12 weeks. Gallein was gradually titrated up to a maximal dose of 10 mg/kg per day and administered by intraperitoneal injection. G, gallein; V, vehicle. **P<0.01 (n=5–7 per group); ****P<0.001 (n=5–7 per group).