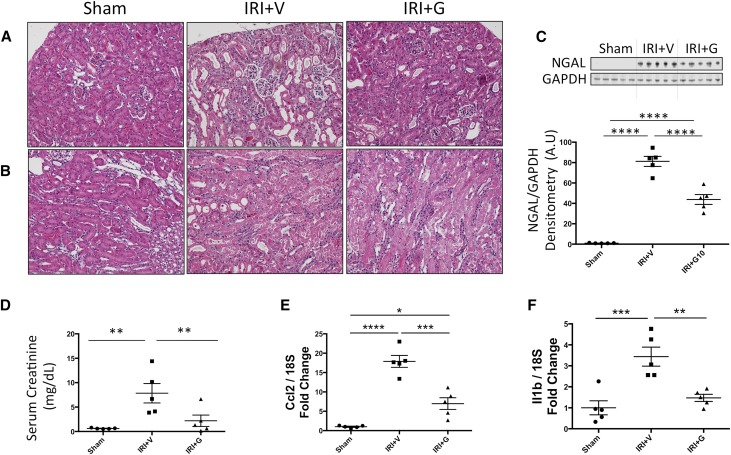
Figure 4.
Gβγ inhibition attenuates tubular injury and renal dysfunction 24 hours after AKI. Bilateral renal IRI causes extensive renal tubular damage in AKI mice 24 hours after surgery in both (A) cortical and (B) medullary regions as shown by hematoxylin-eosin staining (×20). (C) Protein expression of the tubular injury marker NGAL is significantly elevated in the kidneys 24 hours post-IRI. (D) Serum creatinine is elevated 24 hours post-IRI, indicating worsened renal function. (E) Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (Ccl2) and (F) IL-1β (Il1b) inflammatory gene expressions were significantly elevated in the kidneys of AKI mice. All of these pathologic changes are attenuated by gallein pretreatment. Vehicle or gallein (10 mg/kg per day) was administered 2 days before and on the day of surgery. G, gallein; V, vehicle. *P<0.05 (n=5–7 per group); **P<0.01 (n=5–7 per group); ***P<0.001 (n=5–7 per group); ****P<0.001 (n=5–7 per group).