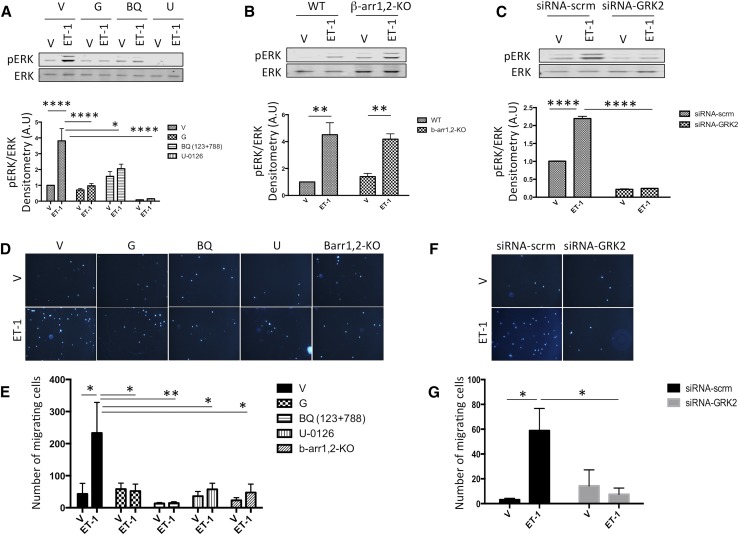
Figure 7.
ET receptor Gβγ signaling mediates in vitro fibroblast activation. (A–C) ET-1–mediated ERK1/2 phosphorylation experiment. Fifteen minutes post–ET-1 stimulation, maximal ERK1/2 phosphorylation is observed, and this effect is inhibited by (A) the small molecule Gβγ inhibitor (gallein; 10 μM) and (B) β-arrestin1,2 knockout (β-arr1,2-KO). (C) GRK2 knockdown by siRNA transfection (siRNA-GRK2) also inhibited ET-1–mediated ERK1/2 phosphorylation relative to the scrambled siRNA transfected group (siRNA-scrm). (D–G) Using the transwell migration assay, MEFs migration was studied 4 hours after incubation with ET-1 (100 nM) in the lower chamber. ET-1 promoted MEF migration, which was inhibited by the small molecule Gβγ inhibitor (gallein, 10 μM), (D and E) β-arrestin1,2 knockout (Barr1,2-KO), and (F and G) siRNA-GRK2. D and F are representative images (×10) of DAPI-stained nuclei (blue) of the MEFs that migrated through the membrane, and E and G are bar graphs showing quantitative analyses of the number of MEFs that migrated through the membrane. ET receptor combined antagonism (ETA antagonist BQ-123 and ETB antagonist BQ-788, 10 μM each) and MAPK inhibition (MEK inhibitor U-0126, 10 μM) blocked the effect of ET-1 on ERK1/2 phosphorylation and MEFs migration. Vehicle or drug treatment was performed before cells were seeded in the upper chamber; n=5 for the ERK1/2 phosphorylation experiment, and n=4 for the transwell migration assay. G, gallein; V, vehicle; WT, wild type. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ****P<0.001.