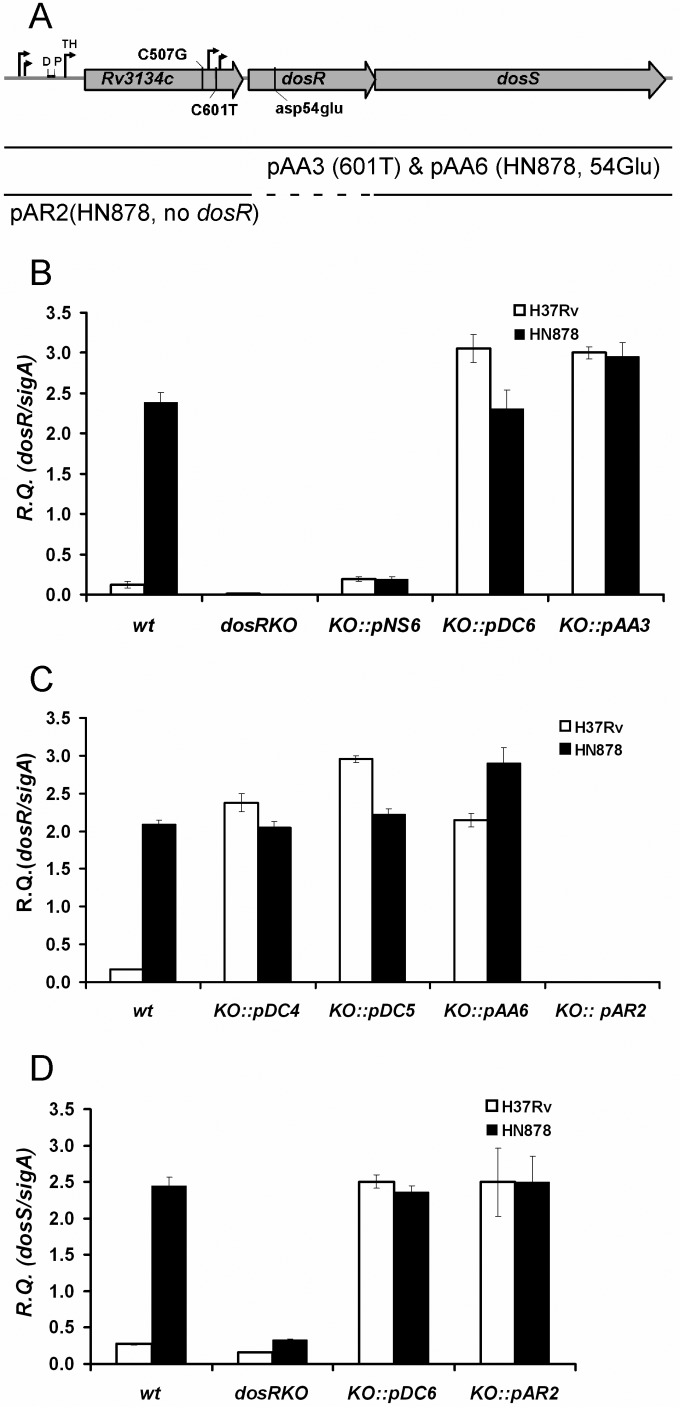
FIG 3.
The C601T promoter SNP is sufficient to cause the Beijing DosR phenotype. (A) Genomic organization of the Rv3134c-dosR-dosS operon, as in Fig. 2. The position of the Asp54Glu mutation (pAA6) is also indicated. A schematic representation of the inserts included in the plasmids used to transform dosR KO mutants of H37Rv and HN878 is shown. pAA3 and pAA6 contain a 4,049-bp fragment that includes 392 bp upstream of the Rv3134c gene in addition to the Rv3134c, dosR, and dosS genes. pAA3 contains a 507C (H37Rv) and 601T (HN878) hybrid allele (i.e., it has only the C601T SNP), while pAA6 contains the 507G and 601T HN878 allele along with a T/A transversion at position 161 of dosR that replaces Asp54 with Glu54. This renders DosR nonphosphorylatable. pAR2 contains a 3,393-bp fragment that incorporates 392 bp upstream of Rv3134c in addition to the Rv3134c and dosS genes (dashed line, no dosR). It is also based on the 507G and 601T HN878 allele. The pNS6, pDC6, pDC4, and pDC5 plasmids are all described in the legend to Fig. 2. (B to D) qRT-PCR analysis of dosR (B and C) and dosS (D) expression in wild-type, dosR KO mutant, and complemented strains. Results are shown as relative quantities (R.Q.), using sigA as the normalizing gene. The error bars represent standard deviation.