Figure 1:
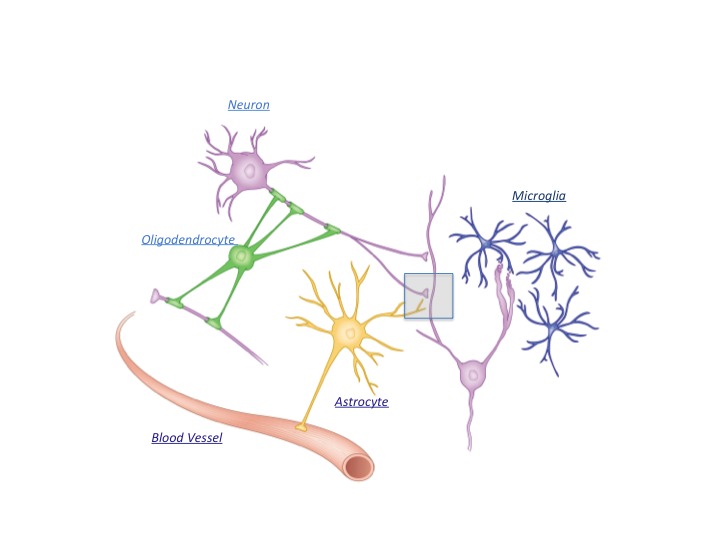
In addition to the electrically active neurons, the brain contains numerous glial cell types, including astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and microglia. Astrocytes are the most plentiful of these glial cells and have unique physical attributes: They contract blood vessels as well as neuronal synapses at a structure called the tripartite synapse (rectangular box and see figure 2). Consequently, they play important roles in synaptic development and modulation/homeostasis as well as in the delivery of nutrients from the circulation to neurons and act as an intermediate to relay neuronal activity to the vasculature to control blood flow.
