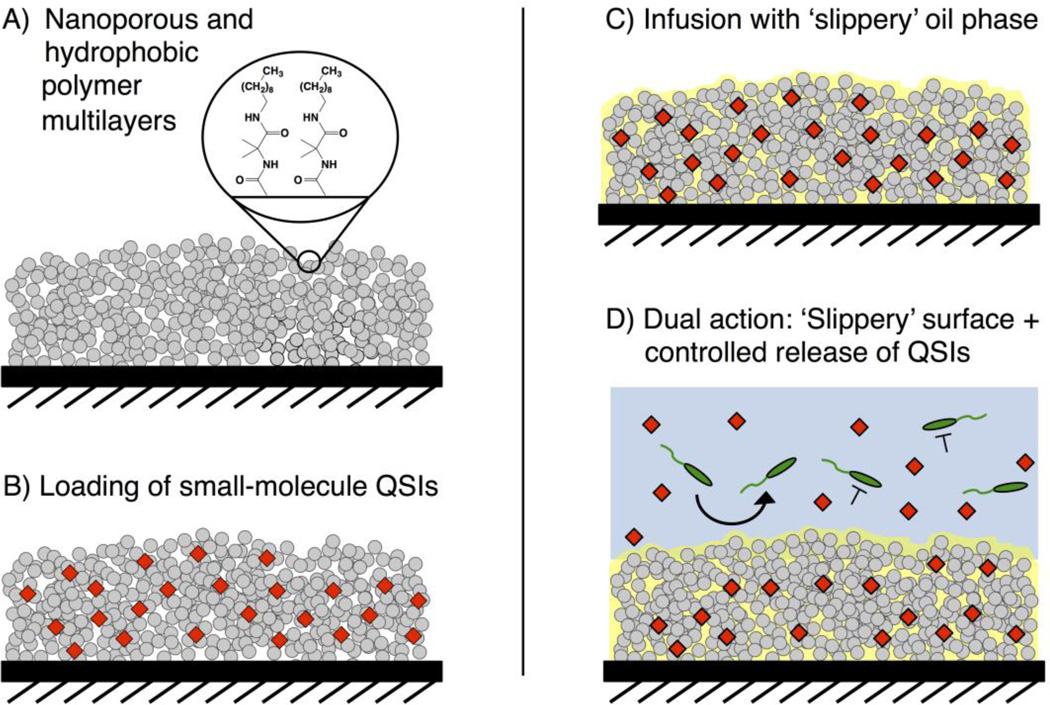
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration showing the fabrication of the QSI-loaded SLIPS used in this study. (A) Reactive and nanoporous polymer multilayers (grey) are functionalized with n-decylamine to render them hydrophobic. (B) Small molecule QSIs (red) are loaded into the multilayers by adding an acetone solution of the agents to dried films and allowing the solvent to evaporate. (C) Silicone oil is infused into the multilayers. (D) The loaded SLIPS gradually release QSIs into aqueous solution; the SLIPS prevent the colonization of bacteria directly on the coated surface while the released QSI modulate the behaviors of nearby planktonic bacteria.