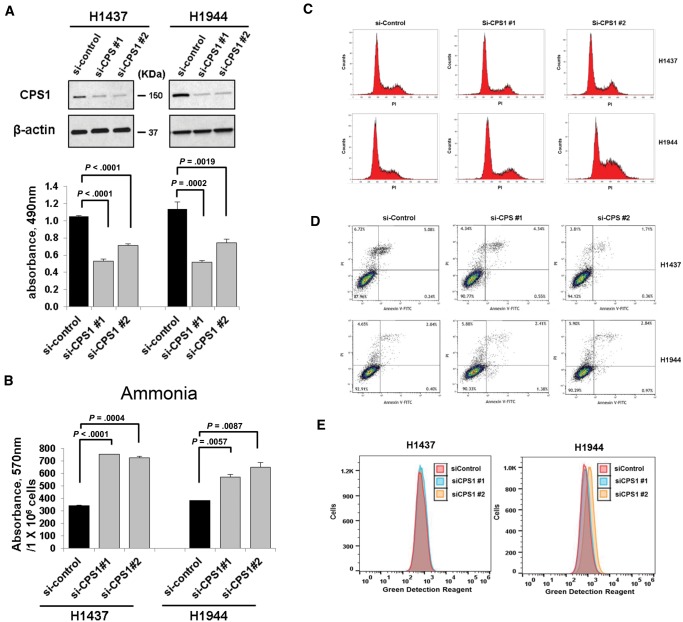
Figure 2.
Effects of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 (CPS1) knockdown in liver kinase B1 (LKB1)–inactivated lung adenocarcinoma cell lines. A) Statistically significant reduction in cell proliferation was observed with MTS = 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5-(3-carboxymethoxyphenyl)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium) assay in H1437 and H1944 cells treated with negative control siRNA or CPS1 siRNA. Knockdown of CPS1 with siRNA was confirmed by immunoblotting. β-actin served as a loading control. B) Ammonia was statistically significantly accumulated in the media of H1437 and H1944 cells treated with CPS1 siRNA compared to negative control siRNA. C) Cell cycle analysis was performed using flow cytometry. D) Apoptosis induction was determined with flow cytometric analysis of annexin V and PI = Propidium iodide staining. E) H1437 and H1944 cells were treated with negative control siRNA and CPS1 siRNA for 72 hours. Cationic amphiphilic tracer dye was used to assess the autophagy using flow cytometry. A and B) Columns indicate the average of triplicate samples from a representative experiment, and bars indicate standard deviation. P values were calculated by two-sided unpaired t test. CPS1 = carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1.