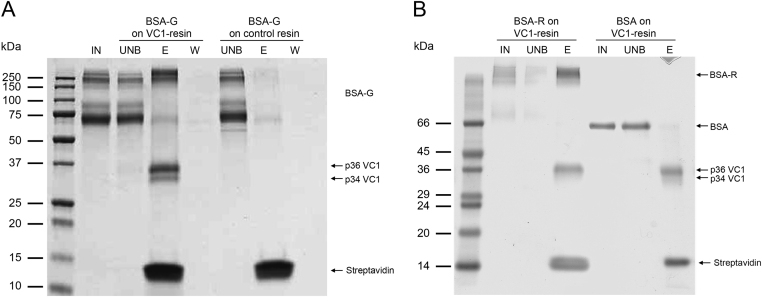
Fig. 3.
Analysis of AGE-BSA binding by pull-down assay using the VC1-resin. (A) Same amounts of AGE-BSA obtained by incubation with glucose (BSA-G) were used as input (IN). BSA-G was incubated with VC1 immobilized on the Streptavidin coated magnetic beads (VC1-resin) or with the Streptavidin-coated magnetic beads alone (control resin) as indicated. The unbound fraction (UNB), the second wash after binding (W) and the eluate (E) from each resin are shown. The E fraction is obtained by boiling the resin with SDS-sample buffer as indicated in Materials and methods and this step removes any associated molecule from the resin including the two forms of VC1 (p34 and p36), and Streptavidin (~14 kDa). Note that VC1 forms were not present in the eluate from the control resin because VC1 was not immobilized on these beads. (B) AGE-BSA obtained by incubation of BSA with ribose (BSA-R) or reagent-grade BSA were used as input (IN). Both samples were incubated with the VC1-resin and the unbound fraction (UNB) and eluate (E) were analyzed. Samples were analyzed under reducing conditions by SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie blue. High MW- species of BSA-G or BSA-R are enriched by the pull-down assay with the VC1-resin and no binding of unglycated BSA occurs on VC1-resin.