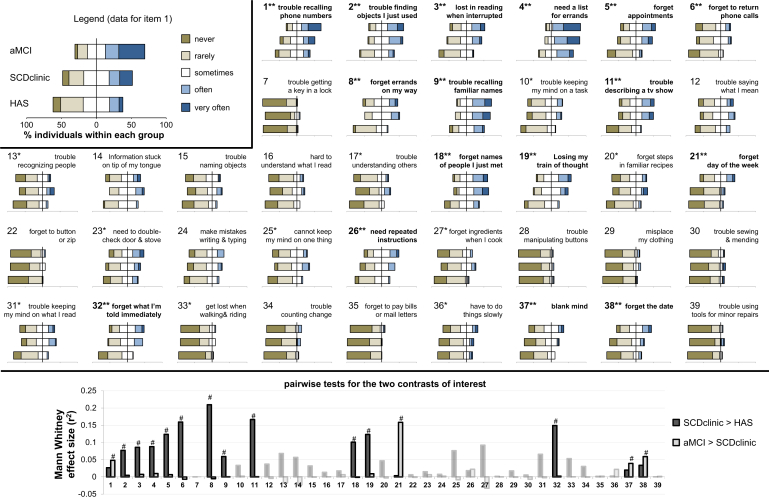
Fig. 1.
Item-by-item responses and group comparisons. The top panel shows the distribution of responses for each item within each clinical group (an alternative version of the figure is available in Supplementary Fig. 2 and numerical data are available in Supplementary Table 2). The top left box illustrates data presentation using diverging stacked bar plots, which enable precise visualization of the responses for each item within each group while showing global between-group trends (stronger endorsement in one group shifts the corresponding bar to the right). Note that the axis scale and increment were kept identical for all items to allow visual comparison. The full phrasing of all items is available in Table 2 but keywords are indicated in the present figure for the sake of simplicity. Kruskal-Wallis test was first used to identify items that showed group differences: ∗indicates an uncorrected P < .05, whereas ∗∗highlights items surviving stringent Bonferroni correction (P < .001282 = .05/39). The two contrasts of interest were tested using Mann-Whitney tests; bottom panel shows effect sizes (r2 = Z2/n) for each contrast (plain color for items surviving Bonferroni correction on the Kruskal-Wallis test and transparent color for others); #indicates significant group difference surviving Bonferroni correction for post hoc tests (P < .025 = .05/2). Numerical data are described in Supplementary Table 2 and details of the statistical tests can be found in Supplementary Table 3. Abbreviations: aMCI, amnestic mild cognitive impairment; HAS, healthy aged subjects; SCD, subjective cognitive decline.