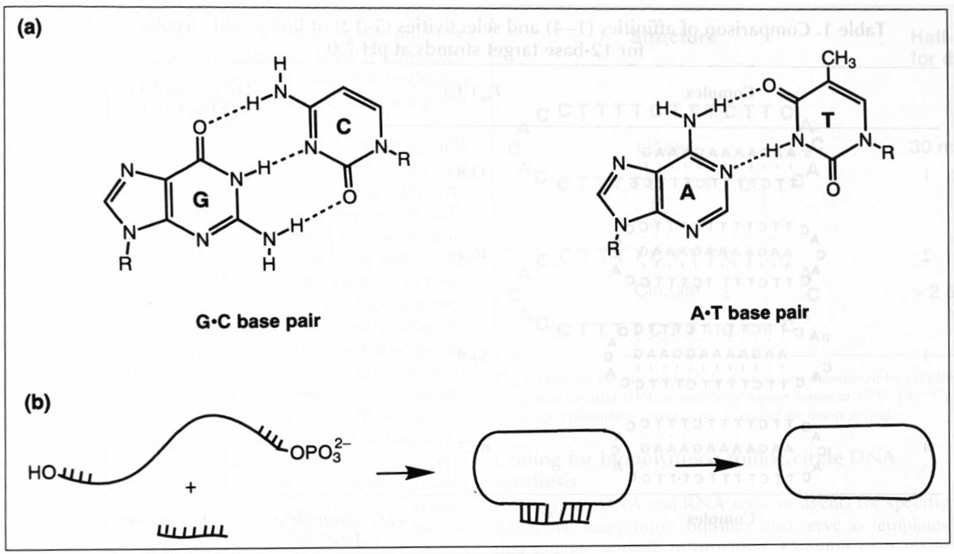
Fig. 1.
(a) The structures of the two classical Watson–Crick base pairs in DNA. G and Care guanine and cytosine; A and T are adenine and thymine. (b) Illustration of how circles are formed from linear DNA/RNA strands using a Watson–Crick complementary ‘template’ or ‘splint’ (a short oligonucleotide) to bring the ends together.