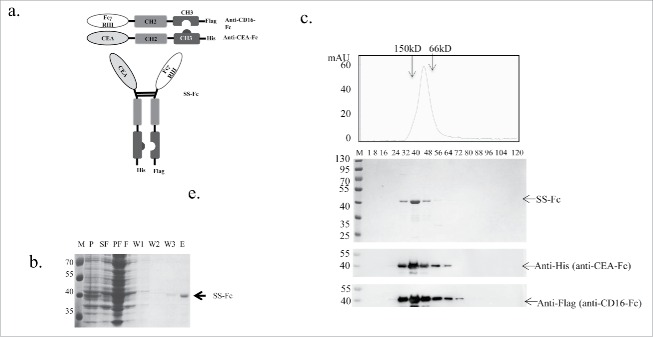
Figure 1.
Construction and purification of the SS-Fc bispecific antibody. (a) Anti-CEA was linked with a human IgG1 Fc fragment with “knob” mutation in the CH3 domain.10 Anti-CD16 was linked with a human IgG1 Fc fragment with “holes” mutations in the CH3 domain.10 The SS-Fc bispecific antibody was formed by heterodimerization of anti-CEA-Fc and anti-CD16-Fc mediated by a CH2–CH3 interaction. (b) Affinity purification of SS-Fc. The panel shows the coomassie blue staining of purification fractions (M, molecular weight ladder, unit: kDa; P, pellet; SF, sucrose fraction; PF, periplasmic fraction; F, flow through fraction of rProtein A affinity purification; W1, W2, W3, wash fraction of rProtein A affinity purification; E, elution of rProtein A affinity purification. (c) Gel filtration analysis of SS-Fc. Standard protein markers ranging from 12.4 to 150 kDa were used to estimate the size of the antibodies. Top panel displays fractions with coomassie blue staining, and bottom panels display the protein gel blots to detect anti-CEA-Fc using an anti-His6 antibody and anti-CD16-Fc using an anti-Flag antibody (arrows indicate the different proteins, respectively).