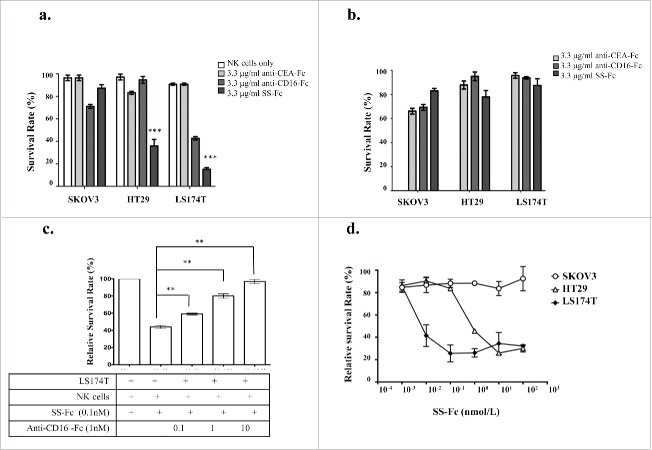
Figure 3.
SS-Fc mediates NK cell-dependent tumor cell killing. (a) The tumor cell lines SKOV3, HT29, and LS174T were incubated with 3.3 μg/ml anti-CEA-Fc, anti-CD16-Fc, or SS-Fc antibodies and freshly isolated human NK cells at a ratio of 10:1 (human NK cells 50,000 cells per well, tumor cells 5,000 cells per well on 96 well plates). The cytotoxicity assay was then performed as described in the Materials and Methods. The data are the mean of triplicates with error bars representing the standard deviation (*** stands for P < 0.001 by t-test, SS-Fc vs. control, anti-CEA-Fc, or anti-CD16-Fc). (b) The tumor cell lines SKOV3, HT29, and LS174T were incubated with 3.3 μg/ml anti-CEA-Fc, anti-CD16-Fc, or SS-Fc antibodies without human NK cells. The cytotoxicity assay was then performed as described in the Materials and Methods. (c) A competition assay was performed by incubating SS-Fc with LS174T cells and NK cells (5000 cells per well and 50,000 cells per well, respectively) with different amounts of anti-CD16-Fc. The cytotoxicity assay was performed as described in the Materials and Methods. The data are the mean of triplicates with error bars representing the standard deviation (** stands for P < 0.01 by t-test, no addition of anti-CD16-Fc vs. different concentrations of anti-CD16-Fc). (d) Dose-response analysis of SS-Fc with HT29 (open square), LS174T (open triangle), and SKOV3 (open diamond) cells. The survival rates at each SS-Fc concentration were normalized against tumor cells incubated with NK cells but without SS-Fc. Representative data from one of 4 different donors were shown here. The data are the mean of triplicates with error bars representing the standard deviation.