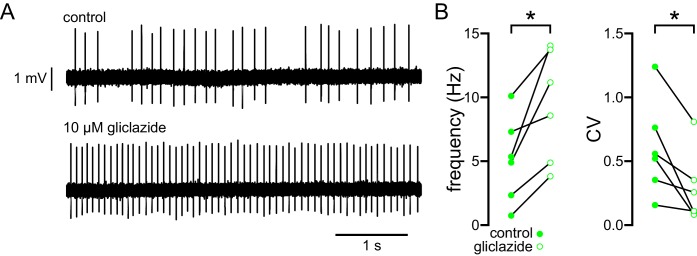
Figure 6. The abnormal autonomous activity of STN neurons in BACHD mice is rescued by inhibition of KATP channels with gliclazide.
(A) Examples of loose-seal cell-attached recordings of a STN neuron from a 6-month-old BACHD mouse before (upper) and after (lower) inhibition of KATP channels with 10 µM gliclazide. (B) Population data (5–7-month-old). In BACHD STN neurons inhibition of KATP channels with gliclazide increased the frequency and regularity of firing. *p < 0.05. Data for panel B provided in Figure 6—source data 1.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.21616.016