Figure 1. The Editing Frequency in CAPS1 mRNA and the Secondary Structure Required for Editing.
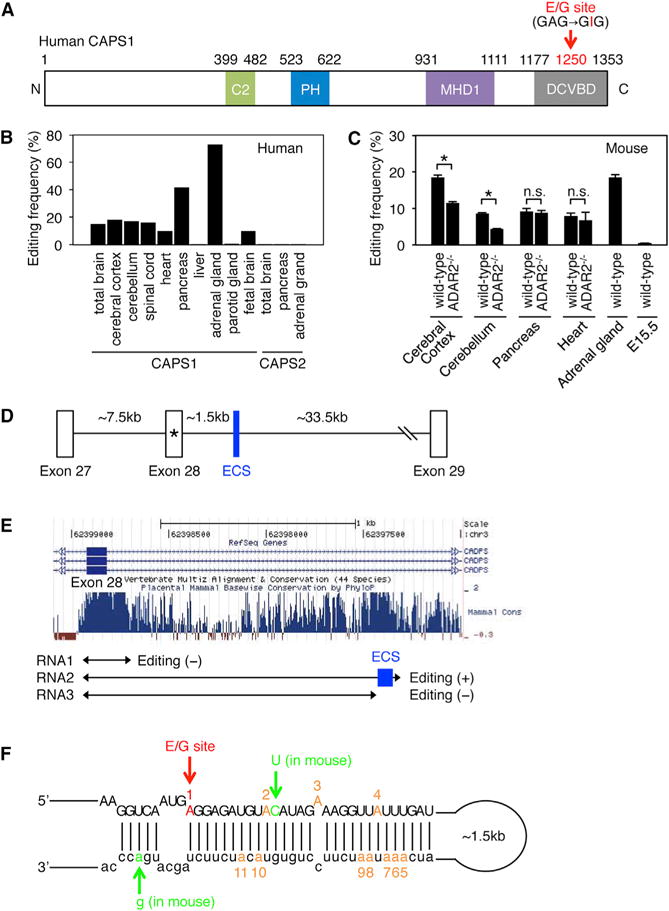
(A) Schematic diagram of human CAPS1. RNA editing in the dense core vesicle-binding domain (DCVBD) changes the codon for amino acid 1250 from GAG to GIG, which converts the glutamate at residue 1250 (E1250) to glycine (G). This E/G site is indicated with a red arrow (see Figure S1A). The position of each domain is assigned by referring to the longest isoform (NP_003707.2). C2, coiled-coil domain; PH, Pleckstrin homology domain; MHD1, Munc13-homology domain 1.
(B) The editing frequency of CAPS1 and CAPS2 mRNAs in various human tissues (see Figure S1B).
(C) The editing frequency of CAPS1 mRNA in various mouse tissues extracted from both wild-type and ADAR2−/− mice. Values are displayed as the mean ± SEM (n = 3, WT and 4, ADAR2−/−; unpaired t test, *p < 0.05). n.s., no significance.
(D) Schematic diagram of human chromosomal DNA encompassing exon 27 to exon 29 of the CADPS gene, which encodes CAPS1. The E/G site is designated with an asterisk. ECS, editing complementary sequence.
(E) The degree of conservation among mammals in the intronic region that is downstream of exon 28, which contains the E/G site, was analyzed using the UCSC genome browser. The regions transcribed to generate the three RNAs (RNA1, RNA2, and RNA3) that were used for the in vitro editing assays are shown below the graphs. The location of the identified ECS is highlighted in blue.
(F) The incomplete double-stranded RNA structure formed by the sequence around the E/G site (in red) and the ECS, which is required for CAPS1 RNA editing, is depicted. The nucleotides that differ between human and mouse are shown in green. The locations of an additional 10 editing sites observed in the in vitro editing assay are shown in orange with the appropriate number (see Figure S1C).
