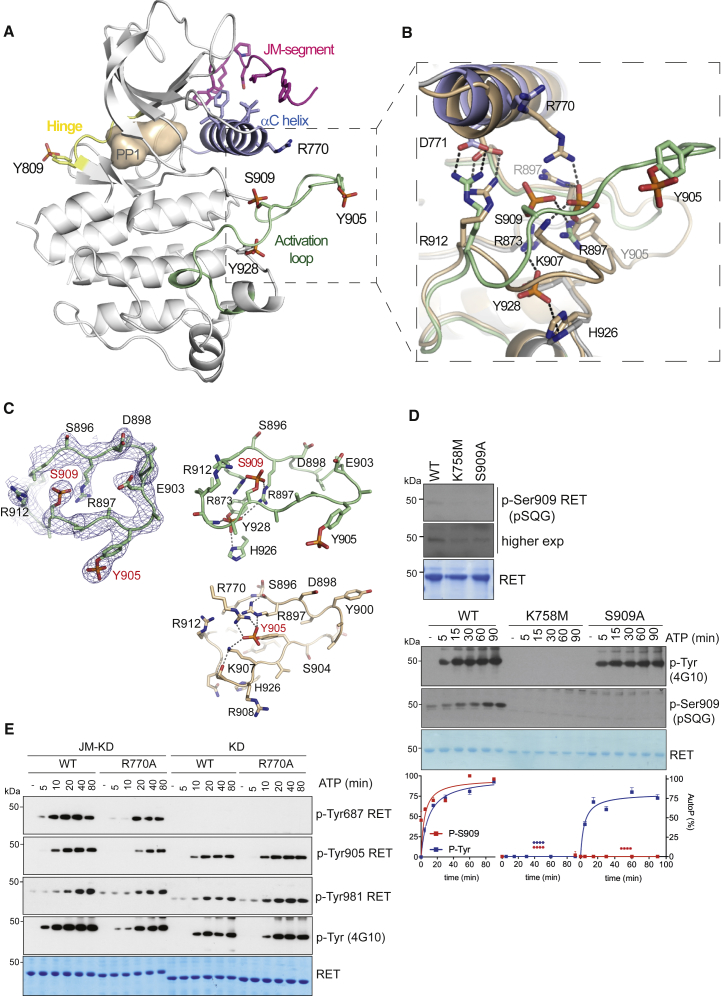
Figure 4.
Crystallographic Identification of an Unexpected Activation-Loop Phospho-S909 Reveals Intrinsic RET Dual-Specificity Activity
(A) Cartoon representation of phosphorylated RET JM-KD structure bound to PP1 inhibitor. Selected residues (including phosphorylated side chains) and secondary structure elements are depicted with discrete colors: JM-segment residues D707 to K716 (magenta), αC helix (purple), hinge residues (yellow), and activation segment residues (green) are shown.
(B) Close-up of the activation-loop conformation and side chains in (A) (green) superposed with RET KD (tint wheat, PDB: 2IVV).
(C) The 2Fo-Fc electron density map of phosphorylated activation-loop from PDB: 5FM2 is shown as blue mesh countered at 1σ. Cartoon representation of basic residues engaged by either phospho-S909/Y928 from the JM-KD structure (upper panel, PDB: 5FM2) or phospho-Y905 (from PDB: 2IVV).
(D) WB analyses using a specific antibody against RET phospho-S909 epitope (pSQG) using recombinant RET ICD WT, K758M, and S909A (upper panel) and in vitro time-course autoP assay in the presence of ATP (5 mM) and MgCl2 (10 mM) for 0–90 min (lower panel). Total RET protein was evaluated by Coomassie blue staining. Quantitation of WB data of Figure 4D is depicted. Data represent the mean of autoP (percentage) normalized to total protein ± SEM of the indicated antibodies, n = 3. Statistics: ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, two-way ANOVA Bonferroni test versus control (WT).
(E) WB analysis of in vitro time-course autoP assay using RET JM661-KD and RET KD core wild-type (WT) and R770A mutants after adding ATP (5 mM) and MgCl2 (10 mM) for 0–80 min using the indicated antibodies.