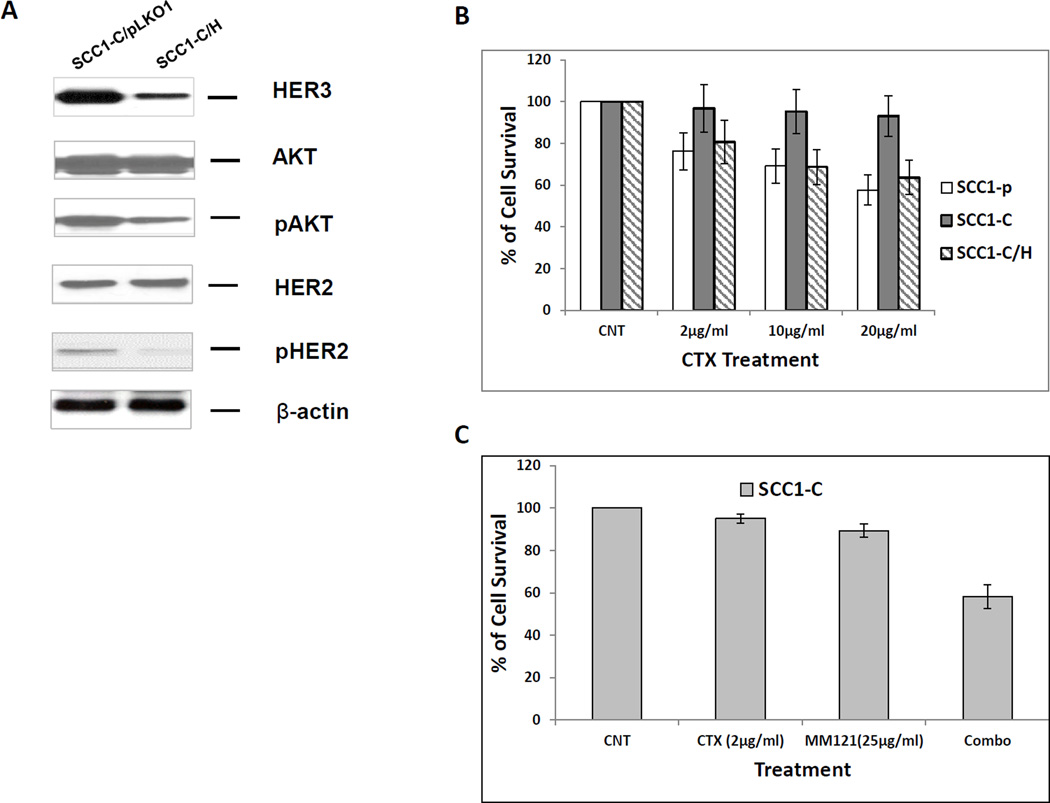
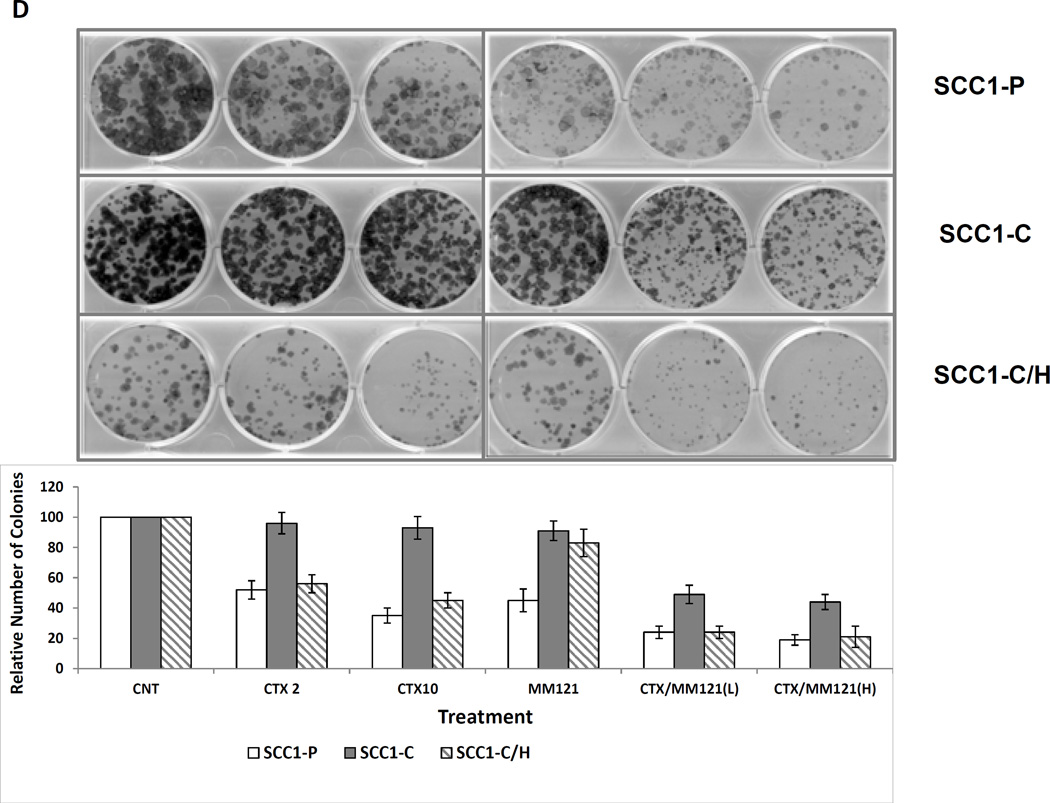
Fig 3. Inhibition of HER3 re-sensitizes resistant UMSCC1-C cell line to cetuximab.
(A) HER was knocked down in UMSCC1-C/H cells. HER2 and AKT activities were also reduced, as demonstrated by a decrease in both pHER2 and pAKT levels. (B) SRB assay shows that cetuximab reduces the growth rate of sensitive parental UMSCC1-P cells at the indicated concentrations after treatment for 48 h. No growth inhibition was observed in UMSCC1-C cells. Knock down of HER3 by shRNA re-sensitized UMSCC1-C cells to cetuximab inhibition. (C) Combination of cetuximab (2µg/ml) and MM-121 (25µg/ml)(combo) more potently inhibited UMSCC1-C growth in SRB assay. (D) In a colony formation assay, cetuximab inhibited colony formation of UMSCC1-P cells but not UMSCC1-C cells at the indicated concentration. When HER3 was knocked down by shRNA, cetuximab inhibition of colony formation was restored. Inhibition of HER3 by its antibody MM-121 (25 µg/ml) also resensitized UMSCC1-C to cetuximab treatment. (CTX2: cetuximab 2µg/ml, CTX10: cetuximab 10µg/ml, CTX/MM-121(L): combination of cetuximab 2µg/ml and MM-121, CTX/MM-121(H): combination of cetuximab 10µg/ml and MM-121). Image represents 3 individual experiments.