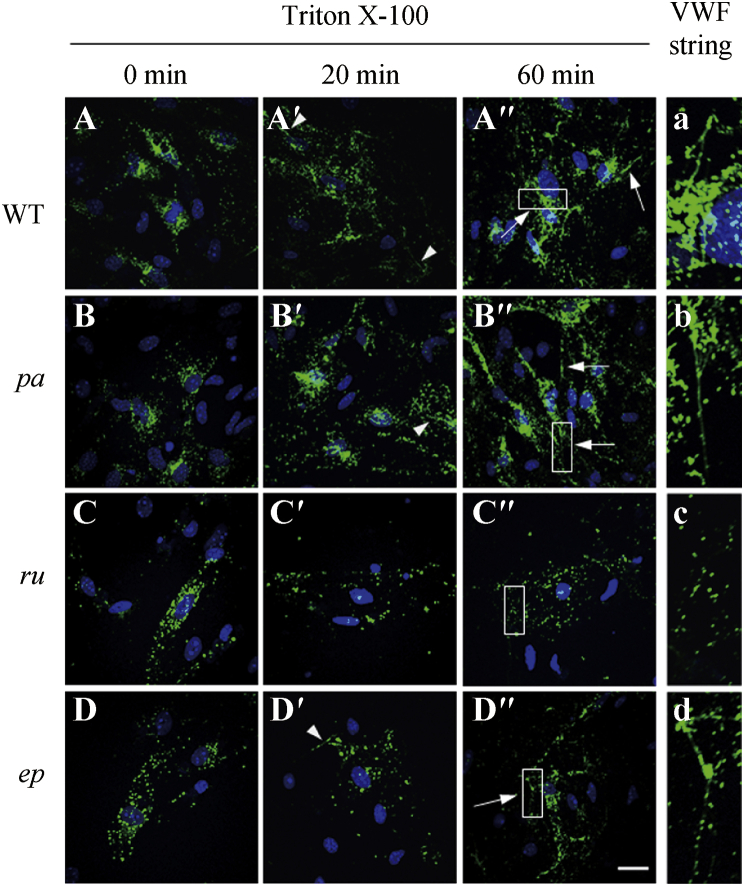
Fig. 5.
VWF dispersion and the ability to generate large surface structures were affected in ru ECs. A–D: Representative immunofluorescence images of the primary ECs are shown. ECs from WT, pa, ru and ep mice (4-week-old male mice) were cultured for 10 days (A–D), then treated with 1% TritonX-100 in growth medium for 20 min (A′–D′) or 60 min (A″–D″) on ice. After immunofluorescence staining of VWF (green), the in situ dispersion and formation of VWF “blobs” and tangles were observed under a confocal microscope. The arrowheads represent potential classic filaments, occasionally present even though these cells were not exposed to flow. The arrows represent longer filaments. No apparent longer filament was visible in ru ECs even after treated for 60 min. Scale bar: 5 μm. a–d: The corresponding magnified regions (white boxes) of A–D show the longer filaments in WT, pa and ep ECs but not in ru ECs after treated for 60 min.