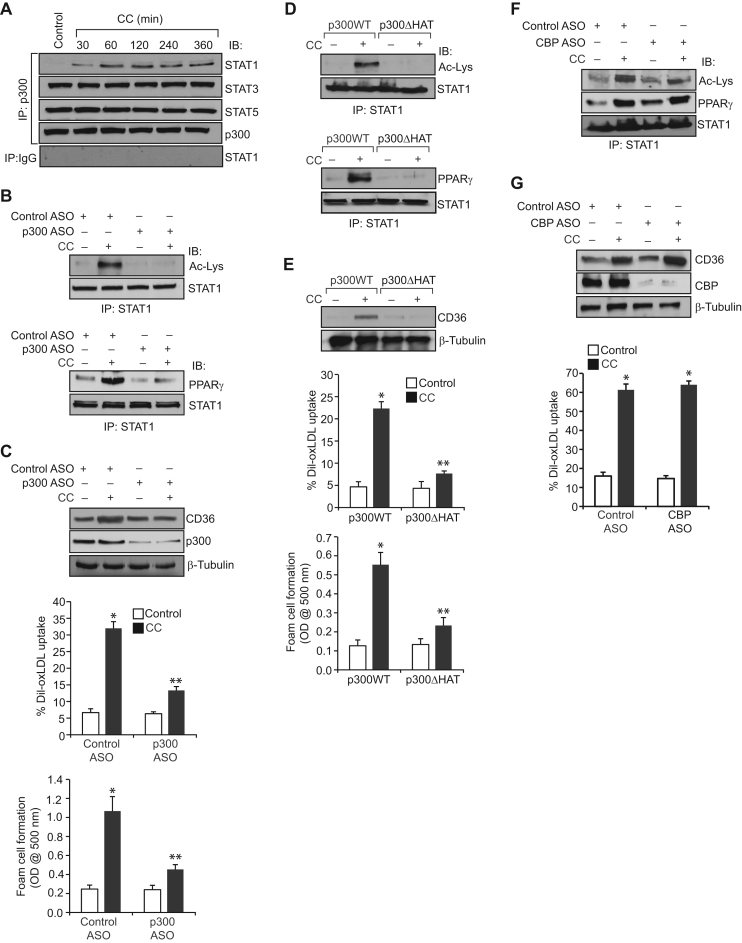
Fig. 3.
CC-induced STAT1 acetylation requires p300 acetyltransferase activity. A. Equal amounts of protein from control and the indicated time periods of CC (40 μg/ml)-treated cells were immunoprecipitated with anti-p300 antibodies or IgG and the immunocomplexes were analyzed by Western blotting for STAT1, STAT3, or STAT5 levels and normalized for p300. B. Quiescent cells were transfected with control or p300 ASO, quiesced, treated with and without CC for 1 h, cell extracts were prepared and equal amounts proteins from each condition were immunoprecipitated with anti-STAT1 antibodies and the immunocomplexes were analyzed by Western blotting for STAT1 acetylation and its association with PPARγ as described in Fig. 1, panel F and Fig. 2, panel C, respectively. C. All the conditions were same as in panel B except that cells were treated with vehicle or CC and analyzed for CD36 expression, oxLDL uptake or foam cell formation as described in Fig. 1, panel C. The blot was reprobed for p300 and β-tubulin to show the effect of the ASO on its target and off target molecules levels. D and E. Cells were transfected with p300WT or p300ΔHAT, quiesced, treated with and without CC and analyzed for STAT1 acetylation, its association with PPARγ, CD36 expression, oxLDL uptake or foam cell formation as described above in panels B and C, respectively. The blots were reprobed for STAT1 or β-tubulin for normalization. F and G. Cells were transfected with control or CBP ASO, quiesced, treated with and without CC and analyzed for STAT1 acetylation and its association with PPARγ, CD36 expression and oxLDL uptake as described above in panels B and C, respectively. The blots were reprobed for CBP, STAT1 or β-tubulin to show the effect of the ASO on its target and off target molecules levels. The bar graphs represent Mean±S.D. values of three experiments. *p<0.01 vs control ASO or p300WT; **p<0.01 versus control ASO+CC or p300WT+CC.