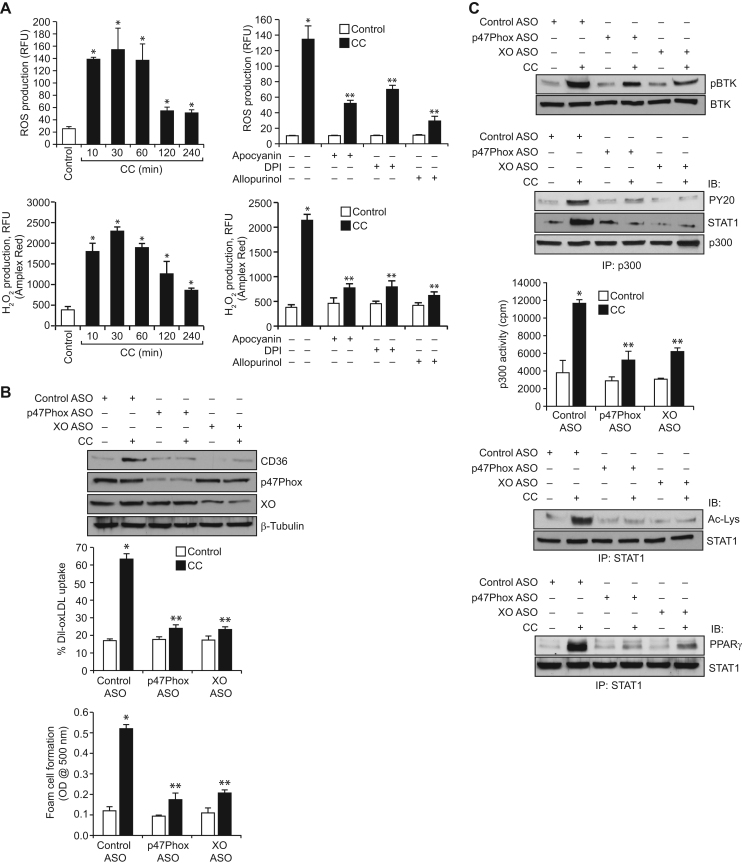
Fig. 5.
CC-induced BTK activation depends on NADPH and xanthine oxidases-mediated ROS production. A. Quiescent cells were treated with vehicle or CC (40 μg/ml) for the indicated time periods or for 30 min in the presence and absence of Apocyanin (100 μM), DPI (10 μM) or Allopurinol (100 μM) and ROS production was measured using CM-H2DCFDA and Amplex Red. B. Cells were transfected with control, p47Phox or xanthine oxidase ASOs, quiesced, treated with vehicle or CC and analyzed for CD36 expression, oxLDL uptake or foam cell formation as described in Fig. 1, panel C. The CD36 blot was reprobed for p47Phox, xanthine oxidase and β-tubulin levels to show the effects of the ASOs on their target and off target molecules levels or normalization. C. Cells that were transfected with control, p47Phox or xanthine oxidase ASOs and quiesced were treated with vehicle or CC for 1 h and analyzed for BTK and p300 tyrosine phosphorylation, p300 association with STAT1, STAT1 acetylation and its interaction with PPARγ as described in Fig. 4, panels B, A and D, respectively, and the blots were reprobed for BTK, p300 or STAT1 levels for normalization. An equal amount of protein from control and each treatment was also assayed for p300 acetyltransferase activity. *p<0.01 vs control ASO; **p<0.01 vs CC or control ASO+CC.