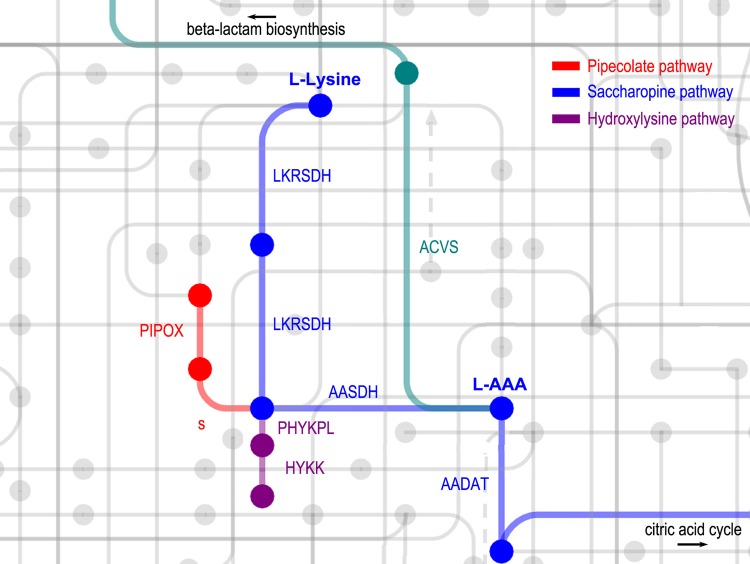
Fig. 1.
L-α-aminoadipic acid metabolism in F. candida. The saccharopine pathway (blue) consists of a bifunctional lysine-ketoglutarate reductase/saccharopine dehydrogenase (LKRSDH), L-aminoadipate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase (AASDH), and kynurenine/2-aminoadipate aminotransferase (AADAT). The pipecolate pathway (red) consists of pipecolic acid oxidase (PIPOX) before it joins the saccharopine pathway. The hydroxylysine pathway (magenta) consists of hydroxylysine kinase (HYKK) and 5-phosphonooxy-L-lysine phospho-lyase (PHYKPL). ‘s’ indicates a spontaneous (non-enzymatic) reaction. L-α-aminoadipic acid (L-AAA) is used in the first step of beta-lactam biosynthesis by δ-(L-α-aminoadipoyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-valine synthetase (ACVS). Figure produced using KEGG PATHWAY Database (http://www.genome.jp/kegg/pathway.html; Kanehisa et al., 2015).