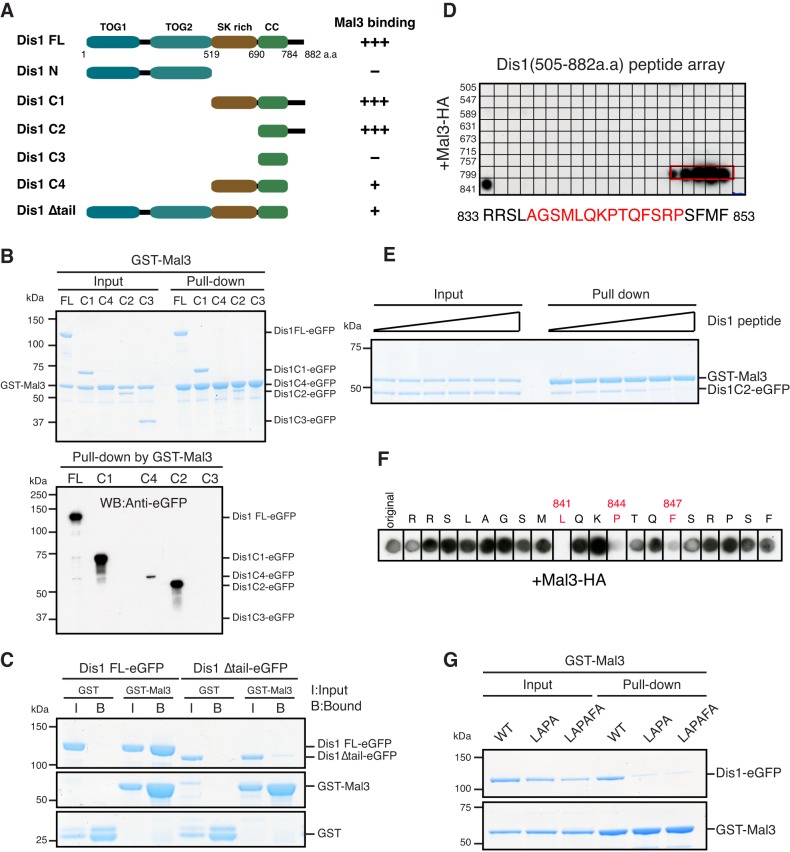
Fig. 3.
The C-terminal tail region of Dis1 is the primary binding site for Mal3. (A) A schematic representation and a summary of their binding to Mal3. TOG1, TOG2, TOG homology domains; SK rich, rich in serine and lysine residues; CC, coiled-coil. (B) Binding between various truncated Dis1 proteins and Mal3. GST–Mal3 bound to glutathione beads was mixed with truncated Dis1–eGFP. The vertical line found between the last two lanes on the right was introduced unintentionally during scanning of the original data. (C) Binding between the full-length or tail-less Dis1 protein and Mal3. (D) Peptide array analysis. The arrays cover from 505th to 882nd amino acid residues of Dis1. The arrays were incubated with a solution containing Mal3–HA protein, followed by immunoblotting against an anti-HA antibody. Amino acid sequences corresponding to bound residues (red) are shown on the bottom. (E) Binding between the tail region of Dis1 and Mal3. GST–Mal3 bound to the glutathione beads were pre-incubated with various concentrations of the Dis1 peptide (amino acids 833–852) (from left to right, 0, 0.5, 2.5, 5.0, 50, 100 µM) for 30 min before incubation with 0.5 µM Dis1 C2–eGFP for an additional hour. (F) Alanine-scanning mutagenesis analysis. Each position in the Dis1 peptide was replaced with alanine. Amino acid residues shown in red were sensitive to alterations. (G) Binding between Mal3 and the wild-type (WT) or mutated Dis1 protein. Dis1–eGFP proteins were LAPA (L841A and P844A) or LAPAFA (L841A, P844A and F847A).