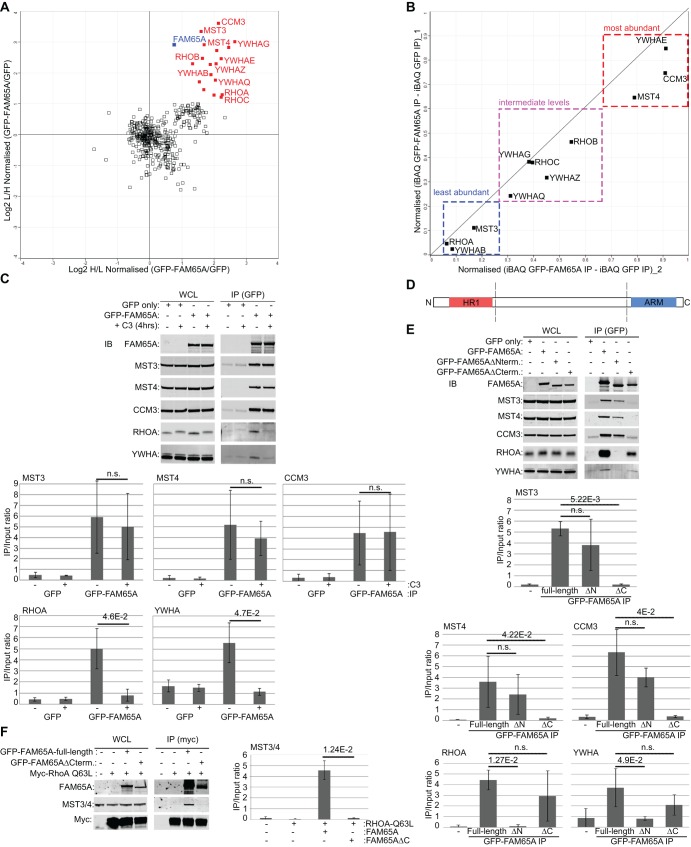
Fig. 2.
FAM65A is an adaptor protein that links RHO to CCM3, MST3 and MST4. (A) FAM65A interacts with all RHO proteins, as well as CCM3, MST3, MST4 and several YWHA isoforms. Averaged Log2 of SILAC ratios from replicates of two reciprocally labelled mixtures of GFP–FAM65A versus GFP-only anti-GFP immunoprecipitations (IP) (Table S2) were plotted. Proteins that significantly (P<0.05) interacted with GFP–FAM65A are marked in red. FAM65A, RHOA, RHOB, RHOC, CCM3, MST3, MST4 and various YWHA isoforms are depicted on the graph. FAM65A (bait) is marked in blue. H/L, heavy:light ratios. (B) Analysis of the relative stoichiometry of FAM65A-interacting proteins by iBAQ (Table S3). iBAQ values of FAM65A-interacting proteins in GFP–FAM65A immunoprecipitations were subtracted by their corresponding iBAQ values in GFP-only immunoprecipitations and normalised to FAM65A levels before being averaged between two reciprocally labelled experiments. Values from two duplicate experiments were plotted. (C) Interaction of endogenous CCM3, MST3 and MST4 with FAM65A is independent of RHO binding. HeLa cells were transfected with expression vectors for GFP–FAM65A, or GFP-only as control, and subjected to TAT-C3 or mock treatment for 4 h before lysis and immunoprecipitation with anti-GFP antibody. Input lysates as well as anti-GFP immunoprecipitation eluates were subsequently analysed by immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies. Although the RHOA and YWHA interaction with FAM65A was abrogated upon TAT-C3 treatment, interactions of CCM3, MST3 and MST4 were unaffected. Quantification of protein levels in each immunoprecipitation condition relative to the input are displayed below the blots (arbitrary units). Quantifications were performed in three independent experiments. Error bars=s.d. Significance P-value was calculated using two-tailed heteroscedastic t-test analysis. n.s., not significant (P>0.05). (D) Schematic representation of FAM65A regions. The N-terminal of FAM65A contains an HR1 domain (amino acids 138–205) and the C-terminal comprises an ARM domain (amino acids 1050–1202). (E) The N-terminus of FAM65A interacts with RHOA and YWHA proteins, whereas the C-terminal interacts with CCM3, MST3 and MST4. HeLa cells were transfected with expression vectors for GFP-tagged full-length, N-terminal-deleted or C-terminal-deleted FAM65A mutants, or GFP-only as control, and subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-GFP antibody. Input lysates as well as anti-GFP immunoprecipitation eluates were subsequently analysed by immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies. Quantification of protein levels in each immunoprecipitation condition relative to the input are displayed below the blots (arbitrary units). Quantifications were performed on three independent experiments. Error bars=s.d. Significance P-value was calculated using two-tailed heteroscedastic t-test analysis. n.s., not significant (P>0.05). (F) FAM65A acts as an adaptor protein, linking active RHOA to MST3 and MST4. HeLa cells were co-transfected with empty vector or an expression vector for Myc–RHOA-Q63L (constitutively active), along with GFP-tagged full-length FAM65A, or the C-terminal-deleted GFP–FAM65A mutant, or GFP-only as control, and subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-Myc antibody. Input lysates as well as anti-Myc immunoprecipitation eluates were subsequently analysed by immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies. Ectopic expression of full-length but not the C-terminal-deleted FAM65A mutant resulted in co-immunoprecipitation of endogenous MST3 and MST4 with constitutively active RHOA. Quantification of MST3 and MST4 levels in each immunoprecipitation condition relative to the input is displayed on the right-hand side of the blots (arbitrary units). Quantification was performed on three independent experiments. Error bars=s.d. Significance P-value was calculated using two-tailed heteroscedastic t-test analysis. n.s., not significant (P>0.05).