Fig. 8.
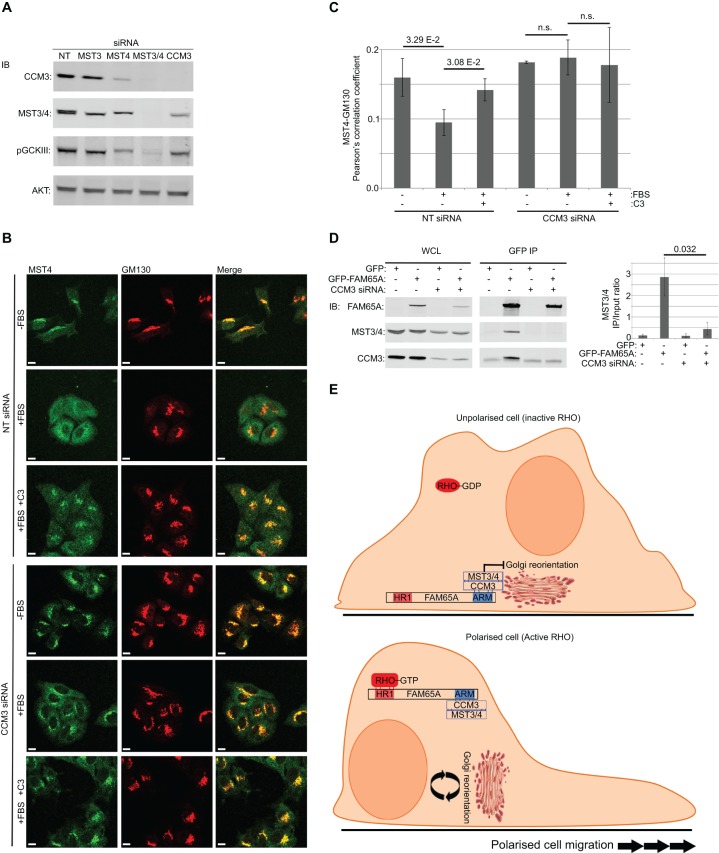
CCM3 acts as an adaptor linking MST kinases to FAM65A. (A) Depletion of CCM3 does not fully abrogate MST activity. HeLa cells were transfected with non-targeting control (NT) or the indicated siRNA pools. At 72 h post transfection, cells were lysed and analysed by immunoblotting with indicated antibodies. Despite a reduction in the total levels of MST3 and MST4, active phosphorylated MST kinases (pGCKIII) were still present in CCM3-depleted cells. (B) RHO-induced MST4 relocation from the Golgi is dependent on CCM3. HeLa cells that had been transfected with CCM3-specific or non-targeting control siRNA pools were seeded at low density, before being serum-starved for 24 h. Cells were treated with TAT-C3 (C3) for 4 h and stimulated with 10% FBS (15 min) as indicated, before being fixed and immunostained with the indicated antibodies for confocal analysis. Scale bars: 10 µm. (C) Quantification of colocalisation from experiments shown in B. The Pearson correlation coefficients between green (MST4) and red (GM130) channels were calculated and averaged from a minimum of three independent fields of view (n=3) from three experiments, each comprised 2–11 cells per field. Error bars=s.d. Significance P-values were calculated using two-tailed heteroscedastic t-test analysis; n.s., not significant (P>0.05). (D) Interaction of MST3 and MST4 with FAM65A is CCM3 dependent. HeLa cells were serially transfected with CCM3-specific or non-targeting control siRNA pools followed by expression vectors for GFP–FAM65A or GFP-only as control and subjected to lysis and immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-GFP antibody. Input lysates (WCL) as well as anti-GFP immunoprecipitation eluates were analysed by immunoblotting (IB) using the indicated antibodies. Depletion of CCM3 abrogates the MST3 and MST4 (MST3/4) interaction with FAM65A. Quantification of MST3 and MST4 (MST3/4) levels in each immunoprecipitation condition relative to the input is displayed on the right-hand side of the blots (arbitrary units). Quantification was performed on three independent experiments. Error bars=s.d. Significance P-value was calculated using two-tailed heteroscedastic t-test analysis. (E) The proposed mechanism for regulation of Golgi reorientation by RHO. When RHO proteins are inactive, the FAM65A–CCM3–MST complex is localised to the Golgi, where MST proteins act to inhibit reorientation. Upon RHO activation, the FAM65A–CCM3–MST complex is relocated away from the Golgi owing to its interaction with RHO, thus relieving the inhibitory effect of MST on Golgi reorientation.