Fig. 6.
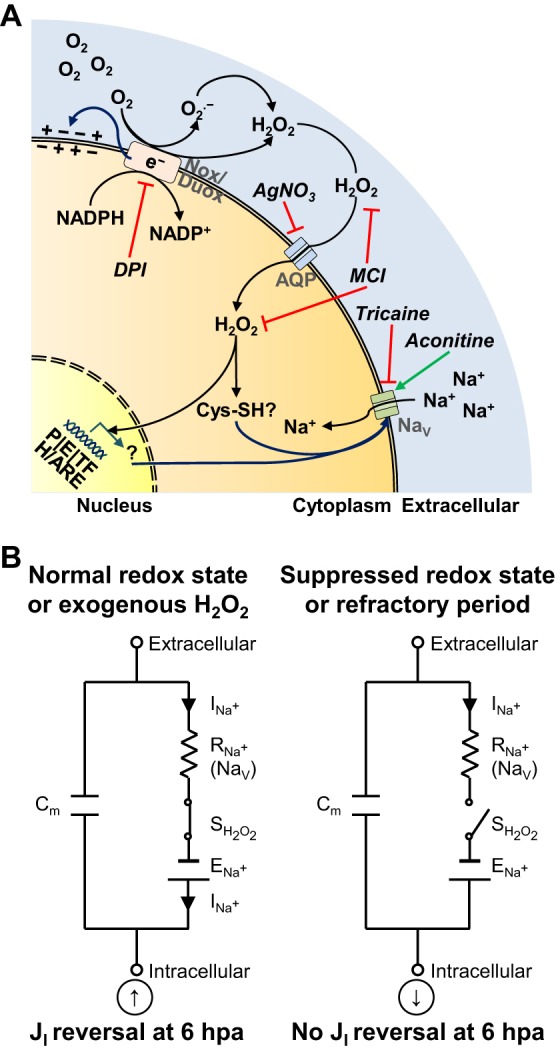
Biochemical and bioelectrical integration during early regeneration via H2O2. (A) Drug targets and H2O2 effects on bioelectricity at distinct steps during a putative H2O2 ‘life cycle’. From top to bottom, steps are production of H2O2 from NADPH oxidases, availability and diffusion of produced H2O2, and H2O2-mediated influences on bioelectric activities or parameters (Vm, TEP, EF, JI and NaV). A representative cell potentially from wound epithelium (overlaying bud) and/or mesenchymal bud of a tadpole amputated at stage 40-41. It is also possible that one cell produces H2O2 and another takes it up to regulate its bioelectric state. For simplicity, we present everything in the same hypothetical cell. e−, electrons; Nox/Duox, NADPH oxidase families (Nox1, Nox2, Nox4 and Nox5 produce superoxide anion (O2.−), whereas Duox1 and Duox2 produce H2O2 directly); AQP, aquaporin; NaV, voltage-gated Na+ channel; Cys-SH, cysteine (Cys) residues of proteins containing thiol (-SH) groups suitable for oxidation; P, promoters; E, enhancers; TF, transcription factors; H/ARE, hypoxia and antioxidant responsive elements; black arrows, ‘life cycle’ of H2O2, from upstream O2 to downstream effect; blue arrows, redox-mediated bioelectric outcome; green arrow, pharmacological activation; red lines, pharmacological inhibition. Drugs are in italic. (B) H2O2 is a switcher in the electrical equivalent circuit. Simplified circuit in a membrane patch of, potentially, a wound epithelium (overlaying bud) and/or mesenchymal bud cell of a tadpole amputated during the regenerative (stage 40-41) or refractory (stage 45-46) period. In the absence of H2O2 (switcher of NaV channels), putative Na+ current (charge carrier) does not cross the membrane through NaV channels and current reversal does not occur at 6 hpa. Suppressed redox state mimics the refractory period circuit. Exogenous H2O2 rescues (from depleted ROS) and induces (from the refractory period) JI reversal. Na+, charge carrier; Cm, capacitance of membrane; ENa+, electromotive force driving Na+; INa+, current of Na+; RNa+, resistance to Na+ flux (synonymous of NaV channels); SH2O2, switcher H2O2. Arrows inside circles indicate net inward (down arrow) or outward (up arrow) current measured extracellularly.
