Fig. 5.
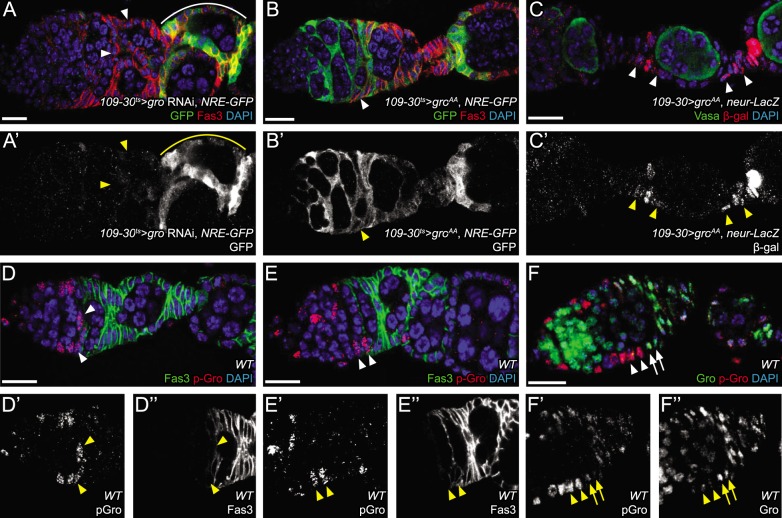
Phosphorylation of Gro prevents Notch signaling and polar cell specification in early pFCs. (A,A′) Expression of gro RNAi causes loss of NRE-GFP activity in early stage follicles (arrowheads). A separate wave of Notch activation occurs surrounding stage 6 follicles (solid line), which is beyond the range of 109-30 expression. (B,B′) Expression of groAA, which is refractory to ERK-mediated phosphorylation, causes ectopic Notch activity throughout the early follicle cell lineage, including FSCs (arrowhead). (C,C′) Expression of groAA causes ectopic activation of neur-lacZ in stalk cells (arrowheads). (D-E″) Phosphorylated Gro (p-Gro) is observed only in FSCs and pFCs within three cell diameters of the niche (arrowheads). (F-F″) Co-staining for Gro (green) and p-Gro (red) indicates that FSCs and early pFCs are p-Gro+, Gro− (arrowheads), whereas later pFCs are p-Gro−, Gro+ (arrows). Scale bars: 10 μm. DAPI is in blue.