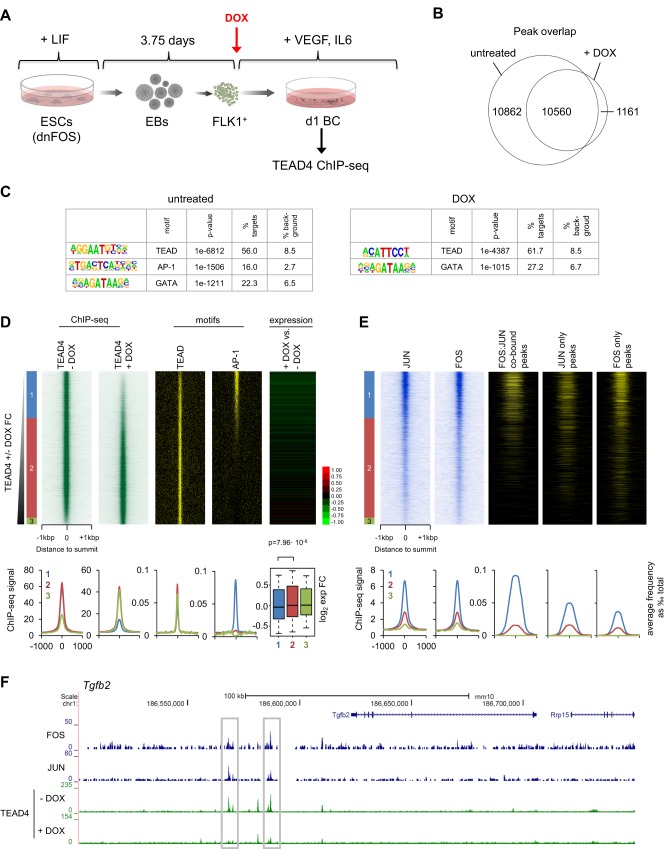
Fig. 6.
AP-1 is required for de novo TEAD4 binding during differentiation of HB to HE. (A) Experimental setup: dnFOS ESCs were differentiated into EBs FLK1+ cells and purified and cultured for 24 h under blast culture conditions with and without 1 µg/ml DOX. Cells of complete cultures were double crosslinked and chromatin was used for TEAD4 ChIP followed by genome-wide sequencing. (B) Overlap of TEAD4 ChIP-seq peaks in DOX- treated and untreated day 1 BC cells. (C) Enriched transcription factor-binding motifs within TEAD4 ChIP-seq peaks from DOX-treated and untreated samples using HOMER de novo motif discovery analysis. (D) TEAD4 ChIP-seq signal from DOX-treated and untreated cells (left), TEAD and AP1 motif presence (middle) and day 1 BC DOX/untreated gene expression fold change (right) ordered by increasing DOX/untreated TEAD4 ChIP-seq signal. Classes of peaks are indicated on the left and defined using cut-offs of ±1 log2 fold change, with class-specific average profiles as well as a boxplot showing gene expression fold change at the bottom. (E) JUN and FOS signals (left) and the presence of FOS:JUN intersecting peaks, and JUN- and FOS-only peaks (right) ordered as in D. Bottom: average profiles for peak presence for classes defined in (D). (F) Representative genome browser screenshot of the Lamc2 locus showing TEAD4 loss at AP-1 binding sites following dnFOS induction.