Fig. 2.
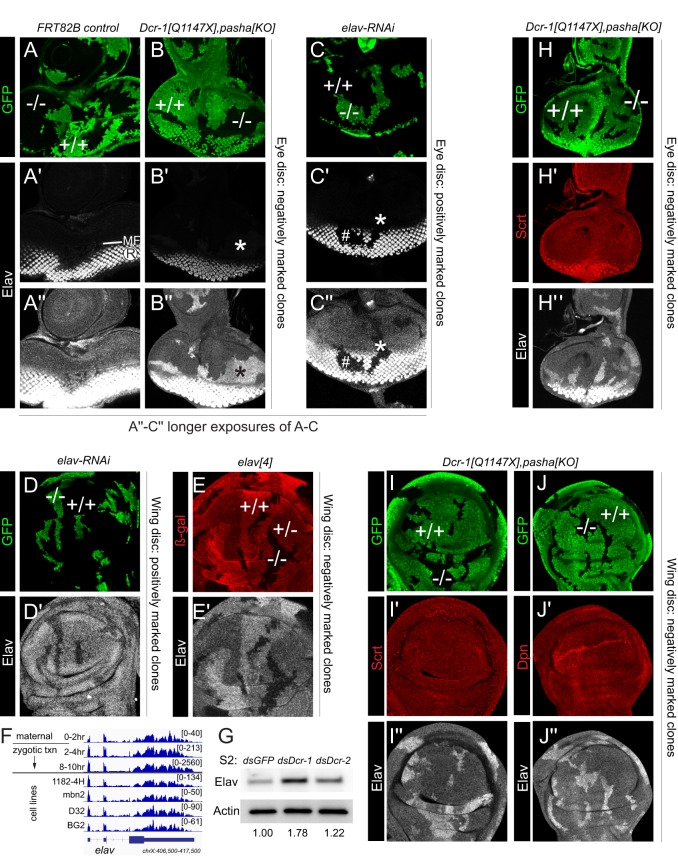
Elav is expressed outside of the nervous system and is specifically derepressed in miRNA pathway clones. Shown are eye imaginal discs (A-C,H) and pouch regions of wing imaginal discs (D,E,I,J) stained for clonal markers (GFP, green or β-Gal, red), Elav (grayscale) and/or other pan-neural markers (red). (A-B″) Comparison of control wild-type clones (A) and Dcr-1, pasha double-mutant clones (B), all made using the Minute system. ‘Conventional' imaging technique for Elav shows typical photoreceptor (R) expression posterior to the morphogenetic furrow (MF), which is not substantially affected by miRNA pathway loss (A′,B′). Longer exposure (A″,B″) emphasizes ectopic Elav anterior to the MF and in the antennal region. (C-C″) Clonal expression of elav-RNAi eliminates Elav in R cells (hash mark), and longer exposure also shows loss of basal Elav in non-neural disc regions (asterisk). (D,D′) Clonal expression of elav-RNAi eliminates basal Elav in the wing disc. (E,E′) Mitotic clonal analysis of null allele elav[4] shows graded expression of basal, non-neural Elav in heterozygous and mutant regions. (F) RNA-seq data across an embryo timecourse show clear maternal expression and zygotic expression of elav long before the earliest presence of neurons (8-10 h). (G) Western blot of S2 cells shows that Elav is specifically derepressed upon Dcr-1 knockdown. Values beneath lanes indicate fold derepression compared with dsGFP control (H-J″) Analysis of canonical neural factors Scratch (Scrt; H,I) and Deadpan (Dpn; J) shows that they are not derepressed in miRNA pathway Minute clones in eye (H) or wing (I,J) discs. At least five imaginal discs were assayed for each genotype, and each set of stainings was performed at least twice; representative clones are shown.