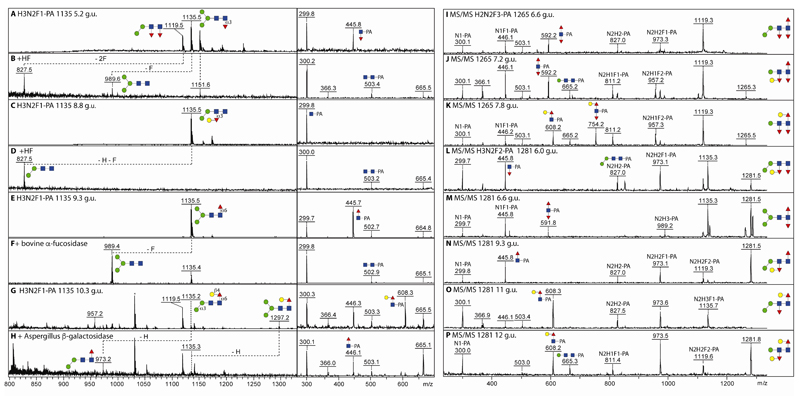
Figure 4. Analysis of fucosylated O. dentatum N-glycans by MALDI-TOF MS.
(A-H) Four isomers of Hex3HexNAc2Fuc1-PA (m/z 1135; PNGase A-released female pyridylaminated N-glycans) separated by RP-amide HPLC (with the indicated elution times in terms of glucose units) were analysed by MALDI-TOF MS ([M+H]+) and MS/MS before and after hydrofluoric acid, bovine α-fucosidase or Aspergillus β-galactosidase treatment; the losses of fucose or hexose are indicated (-F or -H). (I-K) MALDI-TOF MS/MS of RP-amide separated isomers of Hex2HexNAc2Fuc3-PA (m/z 1265) and Hex3HexNAc2Fuc2-PA (m/z 1281; L-P). Key fragments and proposed structures are annotated with a standard symbolic nomenclature or with compositions in terms of fucose (F), hexose (H) and N-acetylhexosamine (N). The presence of m/z 665 or 827 fragments correlates with either one or two mannose residues, whereas the m/z 592, 608 and 754 fragment ions are diagnostic for the modifications of the 2-aminopyridine-tagged reducing terminus (Fuc1-2Gal0-1GlcNAc1-PA).